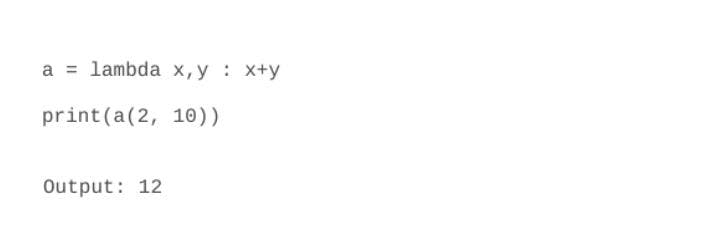Python
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is Python? Enlist some of its benefits.
This basic Python interview question warms up the candidate for the interview and is important even for senior Python positions. How you tackle this question displays your experience and expertise with the programming language. Python is a high-level, object-oriented programming language that enhances user interaction through objects, modules, and automatic memory. Due to Python being a cross-platform programming language, it can run on a myriad of different Operating Systems such as Windows, Linux, Macintosh, and UNIX.
The language finds widespread use in data science, artificial intelligence, and machine learning because of its in-built data structures. Despite being a high-level language, the simplicity of its syntax makes Python a very easy language to grasp. Moreover, because Python supports various modules and packages, making applications using Python becomes extremely easy as less code is required.
2. Can you tell us if Python is object-oriented or functional programming?
Another basic Python interview question that tries to gauge the depth of your understanding of the language. Python is considered to be a multi-paradigm language, which means it supports multiple programming techniques including object-oriented and functional programming. Since most Python tools have bundled up data and functions, it is considered to be object-oriented. The functions of Python are important for data scientists and programmers alike because Python supports both object-oriented and functional programming.
3. What rules govern local and global variables in Python?
In Python, variables are used for labeling and storing data. There are mainly two types of variables in Python - local and global. When a variable is not defined within a function, therefore is referenced within that function, its scope is global and it is called a global variable. When a variable is defined within a function, its scope is local and it is called a local variable.
Additionally, using the keyword, ‘global’, you can explicitly declare a variable, declared within a function, as a global variable. Since the local variable is defined within a function, when accessed outside that function, it will return an error. Global variables, on the other hand, can be accessed throughout the program.
4. Can you tell us what is slicing in Python?
Slicing in Python is about dividing a given string to obtain sub-strings. If you wish to access sequences such as lists, tuples, and strings, slicing is the feature that will help you do so. You can select a specific range or part of these sequences using slicing. You can change or delete parts of sequences like lists that can be changed. Slicing in Python helps you write clean, precise, and readable code. You can perform slicing in Python by either extending indexing or using the slice() Constructor.
5. What is namespace in Python?
This Python interview question delves somewhat deeper into the programming language. In order to give a distinct and unique name to every single object, Python has a system called, namespace. The value of the object, which can be a variable or a method, is connected to the unique name assigned to that object. While searching for the object, the key, which corresponds to the unique name, is mapped with the value assigned to the related object.. Python has its namespace maintained like a Python dictionary.
6. What is pass in Python?
Pass is a placeholder for the future code in Python. When the pass statement is executed, no operation takes place. It basically depicts a blank space, however, in places, like loops, class definitions, conditional statements such as: if statements, or even in function definitions, where empty code is not permitted, a pass can be used to prevent an error.
The pass statement is not ignored by the Python interpreter, as it returns a null value, therefore it is different from a comment, which is ignored by the Python interpreter. This Python interview question can display your alertness and future orientation to the interviewer.
7. Can you explain what is unittest in Python?
Unittest or unit testing is a way to test various codes in Python to ascertain whether they can be used safely or not. This framework is in-built in Python and helps to ensure the quality of code in Python. All the criteria, that are found to be useful and practical during the development process, are coded into the test script by the Python developer. This is done to ensure unit preciseness and accuracy. If any criterion fails, it is reported in the summary. This Python interview question can help the interviewer assess whether you are careful and stringent where the safety of code is concerned.
8. What are negative indexes in Python?
All programming languages use positive indexing in the arrays to locate and access elements. Python is the only language that allows both positive and negative indexing in arrays. A positive index would start from the first element of an array and go forward i.e. the first element would be 0, the second element would be 1, and so on. In negative indexing, the last element of the array would have the index -1, the penultimate element would be -2, and so on.
For example,
arr = [a, b, c, d, e]
print(arr[-1])
print(arr[-2])
Output
e
d
9. What are ODBC modules in Python?
The Microsoft Open Database Connectivity is an interface for the C programming language. It is the standard for all APIs using database C. If you use a Python ODBC interface with the standard ODBC drivers that ship with most databases, you can likely connect your Python application with most databases in the market. The different Python ODBC modules are pyodbc, PythonWin ODBC, and MxODBC.
10. How will you send an email from a Python Script?
You can use a secure connection with the extensions SMTP_SSL() and .starttls(). Following this step, use the built-in smtplib library module to define the SMTP client session object. This object can then be used to send the email message using Python Script. To send the emails you can use HTML content, as well as, the attachments with the email package. If you use a CSV file that contains contact data, you can even send a number of personalized emails. If you add a few lines of code to your Gmail account, you can configure the Yagmail package to send emails. Through this Python interview question, interviewers can understand your knack for applying Python for different uses.
11. What is PEP 8 and its importance?
PEP means Python Enhancement Proposal, is an official design document that provides information for the Python community. It typically documents the style guidelines for Python code
12. What are the key features of Python?
Some of its features are:
- Dynamically typed
- An interpreted language
- Object-oriented
- Coding is quick
13. What does it mean to be dynamically typed in Python?
It means Python type-checks data types during execution. This implies that the Python interpreter type checks as the code runs.
14. What is a scope in Python?
A scope is a block of code in which an object is relevant. Examples of scopes in Python are local scope, module-level scope, outermost scope, and global scope.
15. How can Python script be executable on Unix?
The script file must begin with #!/usr/bin/env Python. This means that the first line must always begin with ‘#’.
16. What is Docstring in Python?
A Docstring is a multiline string used to document a specific code segment. Therefore, developers using Python can easily understand what the code does without having to study the implementation details.
17. What is init in Python?
It is a constructor method automatically called to allocate memory when a new instance or object is created, and classes in Python have an init associated with them which initializes attributes declared in the class when an object of that class is created.
18. What are lists and tuples in Python?
These are sequence data types used in a collection of objects. Both have different data types: lists are represented with square brackets and tuples are represented with parentheses.
Example of list:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Example of tuples:
(13, 90, 11)
19. What is the difference between Arrays and lists in Python?
In order to use arrays in Python, one must import either an array module or a NumPy package, whereas lists are already built into the language and do not require declaration.
20. What is Self-used for in Python?
It is used to represent the instance of the class. This is because in Python, the ‘@’ syntax is not used to refer to the instance attributes.
21. What are the major two-loop statements in Python?
While and For are the major two-loop statements in Python.
Example:

22. What are Decorators in Python?
Decorator is a very useful tool in Python that is used by programmers to alter the changes in the behavior of classes and functions.
23. What built-in types are available in Python?
The built-in types in Python include:
- Strings
- Integer
- Complex numbers
- Floating-point numbers
- Built-in functions
24. How do you differentiate between .py and .pc files in Python?
A file in Python with extension “.py” are source files while with extension “.pyc” are compiled bytecode files generated by the compiler.
25. How do you create a Python function?
In Python, functions can be created/defined using the def statement. To create these functions, firstly we declare them and name them. Then, we start a function definition.
26. How does a function return values in Python?
They do so using the return statement. The statement can be used inside a function to refer the result back to the caller. The return statement has the return keyword and the optional return value. This return value can be used on any Python object.
27. What commands are used to delete Python files?
OS.unlink(filename) or OS.remove(filename)
28. What are modules in Python?
This is a file that includes a set of various functions and statements that can be added to an application. They are basically of two types:
- Built-in Modules
- User-defined Modules
29. What is a Python PATH?
This is an environment variable used to import a variable and check for the presence of variables present in different directories.
30. What is a Package in Python?
A package is a collection of different related modules. It normally contains a file with the name init . py.
31. Create a module in Python.
Creating a module in Python is fairly simple.
- First, open a text editor and create a new file.
- Add the code you want to include in the module. You can include various functions and classes, as well as global variables.
- Save the file with a .py extension (e.g. myModule.py).
- Import the module using the import statement.
- Use the module's functions and classes in your program.
32. What is lambda in Python?
This is the small anonymous function used in Python as an inline function. An example of lambda function is:
lambda arguments : expression
33. How memory can be managed in Python?
In Python, the memory is managed using the Python Memory Manager. The manager allocates memory in the form of a private heap space dedicated to Python. All objects are now stored in this Hype and due to its private feature, it is restricted from the programmer.
34. What are keywords in Python?
These are reserved words with special meanings used to define types of variables. However, they cannot be used for function names or variables. Examples of keywords are: Break, And, Or, If, Elif, For, While, etc.
35. Is Python a case-sensitive language?
Yes, it is a case-sensitive language.
36. What are literals in Python?
Literals are used to represent fixed values for primitive data types in a Python source code.
37. What is Type Conversion in Python?
This is the conversion of one data from one type to another.
38. What do you think is the use of dir () function in Python?
The dir() function can be accessed from the Python interpreter, and it is used to access built-in functions of modules and packages. It is used to display the defined symbols.
39. How can you remove values from an array in Python?
They can be removed using the remove() or pop() function.
Wrapping up
The above content is tailor-made to enable all Python developers to ace Python interview questions because it comprises both technical and non-technical questions and answers across all three levels of basic, intermediate, and senior.
It also helps tech recruiters who wish to hire Python developers and are looking for the latest and best questions out there to test their candidates with. Also, for developers trying to perform well in Turing Python challenge questions can benefit from it. You can also visit here once you have given the Turing test to get an idea of Turing Python test answers.
For tech recruiters, they can opt for an easier and more convenient way of hiring the world’s best remote developers and engineers via Turing. More so, Python developers can also hop on Turing Python test, get tested, and be matched to work with a top U.S. company!
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber Python developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.