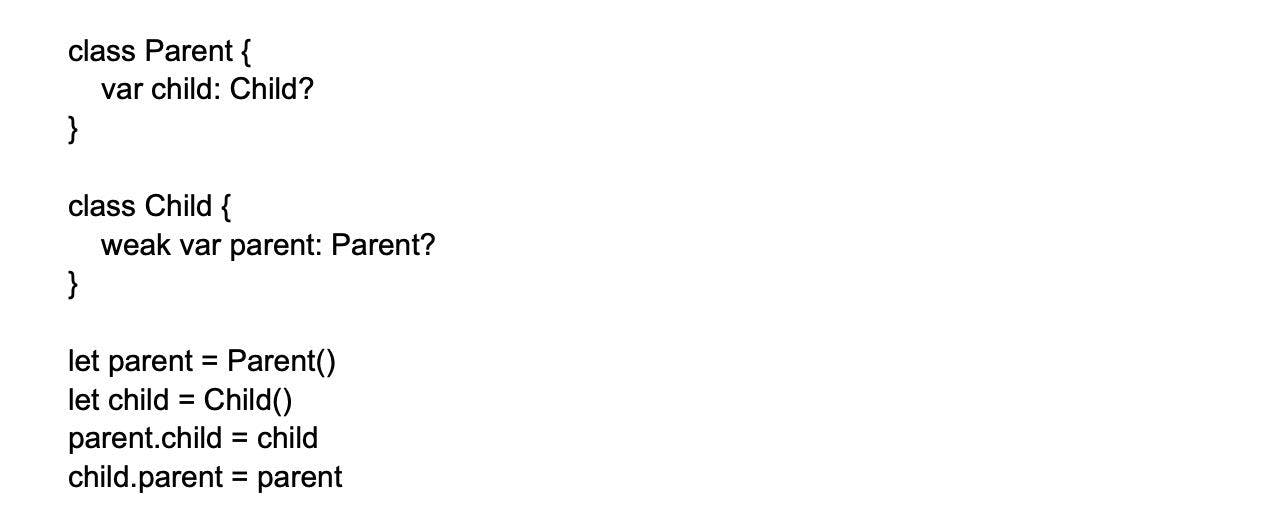iOS
Basic Interview Q&A
1. Talk about CoreData.
CoreData is used as a framework for managing object graphs. It helps manage a graph of object instances that is potentially very large. This allows the app to use a graph that would not completely fit in the memory, by bringing objects in and out of the memory when needed. CoreData also helps in managing the limitations on properties and relationships and in maintaining the integrity of references. This means that when objects are added to or removed from a relationship, the forward and backward links remain consistent. Therefore, CoreData is considered to be the perfect framework for creating the “model” of an MVC architecture.
CoreData uses SQLite for disk storage to implement graph management. It is possible to implement graph management using some other relational database or even a non-relational database like CouchDB. CoreData is more of an API that abstracts from the actual datastore than a database engine. Therefore you can tell how CoreData must store itself - as a plist, an SQLite database, a binary file, or a custom data store type.
Giving a detailed answer to an iOS interview question like this is good, but your answer can become great if you can add your perspective as well to the answer.
2. What is the difference between copy and retain?
Generally, retaining an object increases its retain count by one. This helps retain the object in memory instead of being blown away. Therefore, if you only have the retained version of an object, you will share that copy of the same with whoever sent it to you.
Copying an object, on the other hand, creates an extra copy or a duplicate version of the object. While you share the original with the person who sent the object to you, you do not share the copied or duplicate version with the sender.
3. Talk about code signing for iOS apps.
A signed application helps the system to know who signed the application and also to determine that no changes were made to the application after it was signed. This is a necessary step to submit the application to the App Store for iOS and Mac. There is a signature verification process in OS X and iOS to confirm that the applications do not run with invalid signatures. This builds trust for the users who know that the application is signed by a verified Apple Source and no changes were made to it since signing.
During the build process, your digital identity is used by Xcode to sign your application. The digital identity comprises a public-private key pair and a certificate. The cryptographic functions use the private key to create the signature. Apple issues the certificate that contains the public key and helps identify you as the key pair owner.
The signature protects the executable code of the application because as soon as the executable code in the application changes even slightly, the signature becomes invalid. However, changes to images or nib files do not invalidate the signatures as these resources are not signed.
The signature of an application can be removed and a different digital identity can be used to re-sign the application. For example, all applications on App Store are re-signed by Apple when they are sold.
For an iOS interview question of this type, it may be good to add if you have any prior experience of a project with similar requirements, code-signing for iOS apps in this case.
4. What are the different iOS App States?
There are five app states in iOS. While the app state is managed by the OS, the important tasks are managed by the app itself so that transitions between states happen smoothly. The iOS programming guide lists the five iOS app states as follows:
- Non-running - When the app is not in the running state.
- Inactive - When the app runs in the foreground but does not receive any events. This can happen with an iOS app when a call or SMS is received or some other function takes precedence.
- Active - This is the state when the app runs in the foreground and receives events.
- Background - When the app runs in the background and executes code at the same time.
- Suspended - When the app runs in the background but does not execute any code at that time.
iOS interview questions like the above where you need to talk about multiple states or steps are popular in iOS interviews
5. Mention the main features of Swift. Also, outline its advantages and disadvantages.
The main features of Swift are as follows:
- Generics
- Optionals
- Reference types
- Value types
- Static typing
- Protocols
The biggest feature of Swift is that it is a strongly-typed language. Being a strongly-typed language is an advantage as well as a disadvantage. Development in Swift is easy because of protocols, generics, and optionals which exist because of static typing. While static timing throws several compilation errors and compile-time warnings, it also offers more security at runtime and helps in determinism for optionals, generics, etc. This is, therefore, a big advantage of Swift. The security offered by strict type is most useful under the following circumstances:
- When creating a client application requires more strict clarity than flexibility and dynamism
- When you don’t want inexperienced developers to have excessive power and cause damage to themselves or their work and thus, need to add restrictions
- When your code needs refactoring and using the compiler can help in writing proper and correct code
All the above are scenariOS where developers build customer-facing iOS applications.
The disadvantage of Swift is that it can be too restrictive, especially when the app you are building needs flexibility. For example, when you build a library or a framework, it needs to be flexible and dynamic. In such a case, Objective-C which offers meta-programming capabilities can be a better choice than Swift, though presently, Objective-C seems to be going obsolete.
6. What is MVC?
MVC stands for Model View Controller. It is Apple’s main software design pattern for developing iOS apps. Models represent the data for the application. Views bring things to the screen. Controllers are used to manage the flow of data between model and view. There is no direct communication between model and view, all communication is taken care of by the controller.
As a senior developer, one must know that while MVC is good for general-purpose design, it can be used only for the view layer. Therefore, using only MVC will restrict the architecture of the application and could also lead to the “Massive View Controller” problem.
Massive View Controller refers to that state of the codebase when excessive logic and responsibility are given to View Controllers that are not supposed to shoulder that responsibility. As a result, the code may become rigid, bloated, and difficult to alter. As a remedy, one can use design patterns such as Coordinator, MVP, and MVVM. For scaling the iOS code and avoiding this type of problem, architectures like VIPER and RIBs can be used.
7. Can you differentiate between delegate and KVO?
Both, delegate and KVO, create relationships between objects. Delegation creates a one-to-one relationship in which the delegate protocol is implemented by one object, and the other object uses protocol-defined methods to send messages to the first object. KVO, on the other hand, creates a many-to-many relationship in which the message is broadcast by one object, and one or more objects receive the message and react to it. KVO is not protocol-dependent.
When preparing for your iOS interview, ensure that you go through all such concepts where you could be asked to differentiate between two things.
8. Mention some design patterns apart from the common Cocoa patterns.
Apart from MVC, Singleton, Observer, and Delegate patterns that are commonly used, there are other patterns too that could be used for developing iOS applications:
- Factory Method: With the Factory Method, one can replace class constructors for abstracting and hiding initialization of objects so that the type is determined when the application is run. This method also helps to hide and contain the switch/if statements that help identify which objects to create instances for.
- Adapter: With the help of the Adapter design pattern one can adapt one object’s interface to that of the other. It is useful when a third-party code cannot be changed to one’s own code or when something with an inconvenient or incompatible API needs to be used.
- Decorator: The Decorator is a wrapper that can be wrapped around different classes to enhance their capabilities. One can wrap it around things one wants to decorate. Once wrapped, it implements the interface and delegates the messages that were sent to it to the underlying objects, or it changes and improves objects or gives its own implementation to them.
- Command: The Command design pattern allows you to implement an object representing an operation that you want to perform. The operation you want to execute may have its own state and logic for performing the task. As an advantage, you can hide the operation’s internal implementation from the users, add undo/redo capabilities to it, and even execute operations later instead of at the time of operation creation.
- Template: The Template design pattern has a base class outlining the algorithm for what is required to be done. There are several abstract methods of the base class. These abstract methods must be implemented by the concrete subclasses of the base class. These abstract methods are also referred to as hook methods. The interaction of the Template Method class users happens through the base class that implements the algorithm steps. The subclasses supply the concrete implementations for those steps.
9. Mention different options for implementing storage and persistence in iOS.
Outlined below are the ways to store data in simple to complex order:
- For intermediate data storage or for storage that doesn’t need to last long, we can use in-memory arrays, dictionaries, sets, and other data structures.
- For simple key-value storage, we can use NSUserDefaults/Keychain. Here, one thing is insecure, and the other is secure, respectively.
- For writing data to or from a disk, we can take the help of NSFileManager, whether the data is serialized or not, we can use File or Disk storage.
- When trying to simplify working with databases, frameworks like Core Data and Realm are useful.
- When your requirements include implementing complex querying mechanics, the SQLite relational database is what you should use.
The above iOS interview question is an example of questions where you can use the traditional answer outline above and be safe, but if you add examples of having implemented each or any of the options above, you may earn the interviewer’s attention.
10. When must you use strong, weak, and unowned references?
When you work with Structs or Enums, ARC doesn’t manage these memory types. Thus, there isn’t any need to worry about specifying whether you are using weak or unowned references for the constants or variables there.
In hierarchical relationships, where the parent references the child but the reverse does not occur, you can use strong references. In most cases, anyway, strong references are apt. However, where the relationship of two instances is optional, you must ensure that one instance is weakly referenced to the other.
When one instance is linked to another in a way that it cannot exist in the other’s absence, there is a mandatory dependency of one variable on the other. In such a case, the instance that has mandatory dependence on the other must hold an unowned reference to the other.
11. What programming language is used for iOS development?
The primary programming language used for iOS development is Swift. Objective-C is also used, but its usage has been declining in favor of Swift.
12. Explain overlays.
Overlays are a technique used in operating systems to allow programs to use more memory than they would otherwise be able to.
When a program is loaded into memory, it takes up a certain amount of space. If the program is large and requires more memory than is available, overlays can be used to load only the portions of the program that are currently needed into memory. As the program executes, different portions can be swapped in and out of memory as needed.
13. List some important features of Swift.
Some of the important features of Swift include:
- Safety
- Simplicity in syntax
- Readability
- Support for multiplatform
14. Explain conditional conformances in Swift?
In Swift, conditional conformances allow you to declare that a generic type conforms to a protocol only under certain conditions. This means that a type will only conform to a protocol if some condition is met, such as the type's generic parameter satisfying certain constraints.
15. Explain ButtonStyle protocol in Swift.
ButtonStyle protocol allow to customize new button styles that can be reused without the need for new views. Using this protocol, you can create a button that will appear the way you want. You will make your own style that sets a decent background for a button. You can use the buttonStyle(_:) modifier.
16. Tell one difference between an array and a set.
Where arrays are an ordered collection of values, sets are an unordered collection. Also, an array can duplicate elements, while a set cannot.
17. Explain tuples and their use in Swift.
A tuple is a set of multiple values inside Swift. They occupy space between dictionaries and structures and return values from a function call.
18. What is the use of GeometryReader?
GeometryReader reads all the size and position information and passes that information to its child views via GeometryProxy. It is a flexible view and takes over all the available space provided by the parent view
19. Explain the bounding box.
A bounding box is a rectangular frame that represents the smallest rectangle that completely encloses a particular object or shape. This object can be an image, a text character, or any other graphical element on the screen. The bounding box is defined by its position and size. The position is specified by the coordinates of the top-left corner of the rectangle, while the size is specified by the width and height of the rectangle
20. What purpose does IBDesignable serve?
When a custom view is set to IBDesignable, it allows Xcode to preview it while storyboards are edited. Interface Builder helps directly with making custom layouts. You can easily provide any effects like border width shadow color, shadow width, border color, corner radius, and shadow Opacity.
21. Can you tell the type of settings that are stored in your Info. plist file?
It stores those settings that must be available even when the app is not running. It is a file in the Mac and GNUstep environments that stores user settings. There are three formats plist, Text, Binary, and XML. A plist can store string, number, data(binary data), boolean, dictionary(associative array), and array.
22. Explain raw strings in Swift.
They create strings that print what you see, unlike some escape orders that make your string print in a different form. Raw strings are denoted by the # hash symbol, also known as pound symbol. It is used before and after quotation marks by using # at the starting and ending point.
23. Through what observable objects announce modifications to SwiftUI?
Using two primary ways @Published property wrapper or calling objectwillchange. send()
@Published property wrapper: It is very useful in SwiftUI. It allows us to create observable objects that automatically announce when changes occur.
Objectwillchange: It is a property defined on the ObservableObject protocol. Whenever any @Published properties of the objects change, the compiler synthesizes a default implementation for the property, which emits a value.
24. Tell me about circular references in Swift.
When two objects strongly refer each other, they can never be deallocated. And this strong reference also enables them to keep each other alive. When objects hold strong references to each other, it means that each object has a strong ownership of the other, which creates a cycle, and this cycle is referred to as a circular reference.
25. Can we add a stored property to type through an extension?
No, we cannot add a stored property to a type through an extension in Swift.
Extensions in Swift can add computed properties, instance methods, class methods, and initializers to a type, but they cannot add stored properties. This is because stored properties must be initialized when an instance of the type is created, and extensions cannot provide their own initializers.
26. What do you understand about Half Open Range Operators in Swift?
It specifies a range between values x and y (x..<y) where y is not included. The operator specifies a range that includes the first value but not the final value.It is specifically useful when you work with zero-based lists such as arrays, where it's useful to count up to the length of the list.
27. Explain one benefit of using child view controllers?
One benefit of using child view controllers is that it allows for better modularization and organization of code in an iOS app. By breaking down a large, complex view controller into smaller, more manageable child view controllers, it becomes easier to understand and maintain the codebase.
28. What are reference types?
A reference type contains the location in the memory where data lives. A reference type is passed to a function; instead of creating a new copy of the object, it just creates another reference to that object which is shared among all the different references.
29. Tell me about Nested Function in Swift.
In Swift, a nested function is a function defined within the body of another function. Nested functions are useful for organizing code and encapsulating functionality within a larger function scope. Nested functions can be useful for abstracting complex logic or for breaking down large functions into smaller, more manageable parts.
30. What is Regular Expression?
They are special string patterns that tell how to search for a string. It is a sequence of characters that specifies a search pattern in the text; it finds or finds and replaces operations on strings.
31. What is a Responder Chain?
It is an order of objects that receive the chance to respond to events. It is the series of events that happen once we start interacting with the application on iOS. Applications receive and handle events using responder objects.
32. List the different types of literals Swift has.
- Octal Literals
- Hexadecimal Literals
- Binary Literals
- Decimal Literals
33. Explain processor management.
It provides tools and resources to steer business processes toward better performance. It is an execution unit in which a program operates. It ensures that each process and application receives enough of the processor’s time to function properly and deallocates after the process is completed.
34. Name different types of control transfer statements used in Swift.
- Continue
- Fallthrough
- Return
- Break
- Throw
35. List two types of classes in Swift.
Subclass: It is the act of constructing a new class on an existing class. They inherit characteristics from the existing class, and you can further modify them with new characteristics.
Super Class: When a class inherits properties from another class, the inheriting class is known as a subclass, and the class it inherits from is called a superclass.
36. What is Process management in iOS?
Each thread in iOS serves as a single path of execution. Every application in IOS starts with a single thread that runs the application's main functions.
37. Explain the process of writing a comment in Swift?
For a single-line comment you can use double slashes (//)
And for multi-line comments you can use a forward slash followed by an asterisk (/*)
38. Explain Optional Chaining in Swift.
It is a process of querying and calling properties. Different queries can be chained here, but the chain fails if any link is nil.
39. What do you understand about inheritance in Swift?
It is a process by which a class inherits properties, methods, or any other features from some other class. It is a fundamental behavior that differentiates classes from other types in Swift. We can write different implementations while maintaining the same behaviors by reusing code we have already written.
40. Can you tell me about using Switch Statements in Swift language?
It is used as an alternative to long if-else-if statements. It lets you inspect a value and match it with a number of cases. It's especially effective in making concise decisions based on one variable that can contain a number of possible values. Using the switch statement often results in more concise code that's easier to read.
Wrapping up
We hope the above list of iOS interview questions and answers will give you a good jumpstart for your interview preparation. For hiring managers, these questions and answers will provide as a reference to assess the proficiency of talended iOS developers. Here we have segregated the questions into basic, intermediate, and advanced, so that you can glimpse the important iOS concepts as per the grade of difficulty.
However, if you want to save hours of your hiring time or want to apply for Elite US companies, you can take the help of Turing.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber iOS developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.