Azure
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is Azure and how does it work?
Azure is a cloud computing platform managed by Microsoft. It offers services and tools for building, deploying, and managing applications and services in the cloud. The Azure services can be accessed through the internet.
These include virtual machines, databases, storage, and networking, among others. Users can select the services they need, configure them according to their requirements, and deploy their applications on the Azure platform.
Azure is one of the most widely used cloud computing platforms in the world with millions of active customers in over 190 countries. They range from startups and small businesses to large enterprises and government agencies.
2. What are the different Azure services?
There are numerous Azure services across various categories. Here, we will provide a brief overview of some key services in each category:
Compute:
Azure Virtual Machines: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) solution, providing flexible, on-demand VMs.
Azure Functions: Serverless compute service to run event-driven code without managing infrastructure.
Networking:
Azure Virtual Network: Isolated, private networks in Azure with fine-grained control over traffic between subnets.
Azure Load Balancer: Layer-4 load balancer for distributing network traffic across service instances.
Storage:
Azure Blob Storage: Scalable, secure, and cost-effective object storage for unstructured binary and text data.
Azure File Storage: Managed file shares for cloud or on-premises deployments.
Databases:
Azure SQL Database: Fully managed, intelligent, and scalable relational database service based on SQL Server.
Cosmos DB: Globally distributed, multi-model NoSQL database service with low latency and tunable consistency.
Security and identity:
Azure Active Directory: Identity and access management service for centralized user management, authentication, and authorization.
Azure Key Vault: Secure storage and management of cryptographic keys, secrets, and certificates.
Developer and management tools:
Azure DevOps: All-in-one solution for planning, collaboration, build, test, and deployment of applications.
Azure Monitor: Comprehensive, full-stack monitoring service for application and infrastructure performance.
Analytics and IoT:
Azure Stream Analytics: Real-time, complex event-processing service for streaming data.
Azure Data Factory: Data integration service for orchestrating and automating data movement and transformation.
AI and Machine Learning:
Azure Machine Learning: Scalable, managed platform for model development, deployment, and management.
Azure Cognitive Services: Suite of AI services for vision, speech, text, and language understanding.
3. What is the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Azure?
Iaas - Infrastructure as a Service, Paas - Platform as a Service, and Saas - Software as a Service are the three different categories of cloud computing services offered by Azure.
Here’s a quick look at IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): With IaaS, Azure provides users with virtual machines, storage, and networking capabilities, allowing them to run their own operating systems and applications in the cloud.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): With PaaS, Azure provides users with a platform for building, deploying, and managing applications without the need for the underlying infrastructure. Azure manages the infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking, and users can focus on developing their applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS): With SaaS, Azure provides users with ready-to-use software applications that are hosted in the cloud. Users can access the applications through a web browser or mobile app.
4. What is a virtual machine in Azure? How do you create a virtual machine in Azure?
In Azure, a virtual machine (VM) is a computing environment that behaves like a physical computer but is implemented entirely in software. A VM runs on physical hardware, but its operating system, software applications, and data are all stored in a virtualized environment.
Azure provides a range of virtual machines that users can choose from with different sizes, configurations, and operating systems.
To create a virtual machine in Azure, follow these general steps:
- Sign in to the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com.
- Click on the "Create a Resource" button on the left-hand menu and search for "Windows Server" or "Linux" depending on the operating system you want to use.
- Select the appropriate virtual machine image and size based on your requirements. You can choose from different sizes depending on CPU, memory, and storage capacity.
- Configure the VM settings, including the name, username, and password for the administrator account, network settings, and disk settings.
- Review the summary page and click on "Create" to create the virtual machine.
- Once the VM is created, you can connect to it using Remote Desktop for Windows virtual machines or SSH for Linux virtual machines.
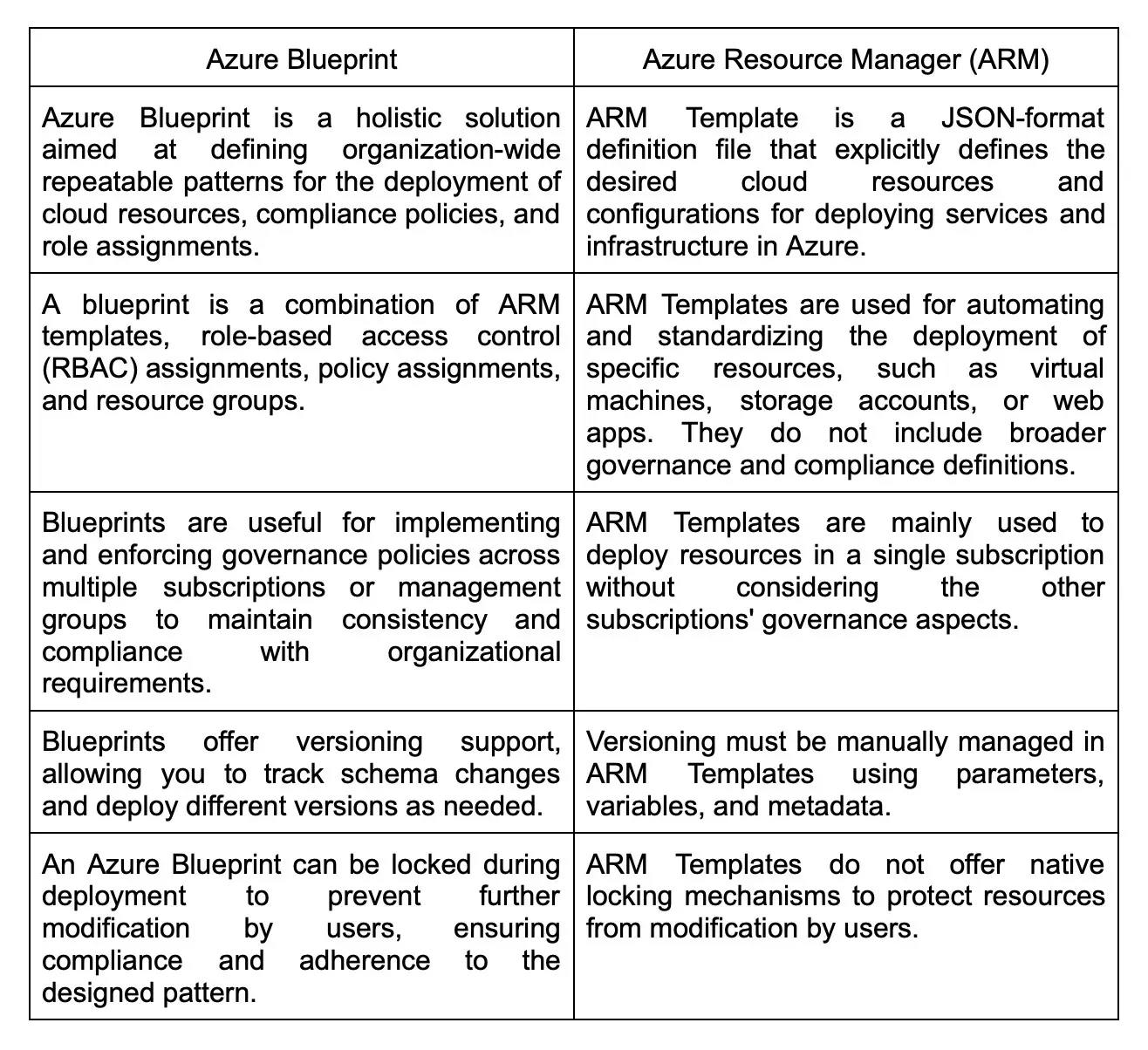
5. What is Azure Resource Manager?
The Azure Resource Manager (ARM) is a service offered by Microsoft Azure to help users with the management and organization of resources deployed on the cloud. It provides a way to group related resources like virtual machines, storage accounts, and network interfaces into logical units for easier management and deployment.
It also enables you to define dependencies between resources, so you can ensure that resources are deployed in the correct order and that any prerequisites are met. ARM provides a centralized and consistent way to manage Azure resources, making it easier to scale and manage complex applications and infrastructures in the cloud.
It provides a unified API for managing resources in a single, coordinated manner. It also enables you to tag and categorize resources and apply policies to enforce compliance across your organization.
6. What is a virtual network in Azure? How can you create a virtual network in Azure?
A virtual network in Azure is a representation of the physical network in the cloud. It enables you to establish a secure connection and isolate Azure resources such as storage accounts, app services, and virtual machines from other networks within your Azure subscription. It enables the creation of a private network in the cloud. You can also define IP addresses, subnets, security policies, and routing tables.
To create a virtual network in Azure, you must follow these steps:
- Log in to the Azure Portal (https://portal.azure.com/).
- Click on the "Create a resource" button (+) in the top left corner.
- In the search bar, type "Virtual network" and select "Virtual network" from the dropdown list.
- Click on the "Create" button.
- In the "Basics" tab, enter a name for the virtual network and select the subscription, resource group, and region where you want to create the virtual network.
- In the "IP addresses" tab, specify the IP address range and subnet(s) for the virtual network.
- In the "Security" tab, configure network security groups (NSGs) to control inbound and outbound traffic to resources in the virtual network.
- Click on the "Review + Create" button to review your settings.
- Click on the "Create" button to create the virtual network.
Once the virtual network is created, you can add resources, such as virtual machines or storage accounts, to the virtual network and configure their network settings.
7. How many cloud service roles does Azure provide?
Cloud service roles comprise a collection of application and configuration files. Azure offers two types of roles: administrative and technical.
Web role: This role provides a dedicated IIS (Internet Information Services) web server for the automatic deployment and hosting of front-end websites.
Worker roles: The worker roles allow the programs hosted within them to run asynchronously for extended periods, are independent of user interactions and do not typically use IIS. They are also suitable for carrying out background tasks. The applications are run independently.
8. What are IaaS, PaaS and SaaS?
It is common to come across this Azure data engineer interview question.
IaaS: This stands for "Infrastructure as a Service." The infrastructure serves as a platform for hosting applications. It provides a collection of capabilities such as operating systems, network connectivity, and so on that are at the infrastructure level and are offered as a pay-per-use policy. Azure VM, VNET, and other examples are available.
PaaS: PaaS stands for "Platform as a Service," and it is primarily concerned with providing underlying infrastructure abstraction to developers to enable faster application development without dealing with hosting maintenance. Azure online apps, storage services, cloud services, and so on are some examples.
SaaS: SaaS stands for "Software as a Service." It refers to programs that are delivered via the service delivery paradigm and are simply consumed and used by an enterprise. These applications are typically activated by charging the organization for their use or through advertisements. Applications such as Office 365, Gmail, and SharePoint Online are examples.
9. What are the benefits of virtual networks?
With a virtual network, you can control network traffic flow between resources, implement security policies to restrict access to resources, and configure network address translation (NAT) to allow access to resources from the internet. You can also connect your virtual network to an on-premises network using a VPN gateway, an ExpressRoute circuit, or a point-to-site VPN connection.
Virtual networks provide scalability and flexibility by enabling you to create multiple virtual networks and creating a connection between various networks. Azure virtual networks provide a secure and flexible way to connect and isolate resources in the cloud, enabling you to build and deploy complex applications and services with ease.
10. What is cspack in Azure?
It is a command-line utility for creating service package files. The tool also assists in preparing the application for deployment in Microsoft Azure or a computing emulator.
Every cloud service project contains a.cscfg file, which is essentially the cloud service configuration file generated by the cspack program and is mostly used to store:
- The number of role instances required for each role's deployment in the project
- The certificates' thumbprint
- Configuration and settings are user-defined
11. What do you understand by Azure Cognitive Services Containers?
Azure Cognitive Services Containers are a way to deploy and run Azure Cognitive Services APIs within Docker containers. It is a suite of pre-built APIs and services that enable developers to add various features to improve the performance of their applications.
By deploying Azure Cognitive Services APIs within Docker containers, developers can take advantage of the benefits of containerization, such as improved scalability, easier management, and increased portability. It can be deployed and managed using container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm.
12. Explain Azure app service. What are the different features and benefits of Azure app service?
Azure app service is an HTTP-based service from Microsoft Azure for building, deploying, and hosting web and mobile applications as well as REST APIs. With it you can develop apps using different programming languages such as Java, PHP, Python, Ruby, Node.js, and .NET, among others.
The Azure app service provides a managed environment for hosting applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. This allows developers to focus on application development and deployment.
You get a wide range of features, capabilities, and benefits with the Azure app service. Here are some of the prominent features:
- Multiple deployment options, including code deployment from GitHub, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps, container-based deployment, and automated deployment from Visual Studio or Azure CLI.
- Scalability options include horizontal scaling with automatic load balancing, and vertical scaling with multiple instance sizes.
- Integration with other Azure services like Azure Active Directory, Azure SQL Database, and Azure Storage.
- Custom domain support, SSL certificates, and SSL binding.
- Built-in monitoring and logging capabilities via integration with Azure Monitor, Application Insights, and Log Analytics.
13. Explain Azure time series insights.
Azure Time Series Insights is a powerful data analytics tool from Microsoft that enables you to collect and store data at a high frequency, typically from sensors or other devices, and analyze that data in real-time to gain insights into performance, anomalies, and trends.
The data is stored in a time-series database that allows for fast and efficient querying of historical data as well as real-time data. Time Series Insights provides a user-friendly, web-based interface that allows you to visualize and analyze data using interactive dashboards and charts.
14. What are the features of the Azure SQL Database?
With Azure SQL Database, you can provision databases in minutes, scale up or down as needed, and benefit from automatic patching, backup, and high availability. It offers a range of features and capabilities, including:
- Compatibility with T-SQL which allows developers to use familiar tools and techniques to build and deploy applications.
- Built-in security features, including advanced threat protection, data encryption, and access control.
- Automatic backups, point-in-time restore, and geo-replication which provides data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Support for multiple deployment options, including single databases, elastic pools, and managed instances.
15. What is Azure Service Level Agreement (SLA)?
The Azure Service Level Agreement (SLA) is a contract that ensures or guarantees that when two or more role instances of a role are deployed on Azure, access to that cloud service is assured at least 99.9 percent of the time.
It also indicates that if the role instance process is not in the operating state, such processes will be detected and corrective action will be taken 99.9 percent of the time.
16. What is Azure Storage service? What are the benefits of Azure Storage service?
Azure Storage is a modern cloud storage solution from Microsoft that offers storage solutions to contemporary requirements. It provides high availability, durability, scalability, and security for various data assets on the cloud.
Azure Storage gives access to data objects from anywhere in the world using HTTP or HTTPS through REST API. You also get client libraries with Azure Storage to build applications/services using various languages like Java, Python, C++, JavaScript, Go, and .NET.
Azure Storage service provides many benefits and features, including:
Scalability: It allows you to scale your storage capacity as needed without the need to provision or manage additional hardware.
High availability: It provides multiple layers of redundancy, ensuring that your data is available and accessible at all times.
Security: It provides built-in security features, including encryption at rest and in transit, access control, and firewalls, to help protect data from unauthorized access.
Durability: It provides high durability for your data with multiple copies stored across different storage nodes and data centers.
Cost-effectiveness: It offers flexible pricing options based on your storage needs, allowing you to pay only for the storage you use.
Accessibility: Azure Storage data is highly accessible from anywhere in the world through HTTP or HTTPS. The service also offers scripting in Azure CLI or Azure PowerShell and easy data visualization solutions via Azure Portal.
17. What are the different cloud deployment models in Azure?
There are three cloud deployment models available in Azure:
Public Cloud: The cloud provider owns the cloud infrastructure publicly. Server resources may be shared among multiple applications.
Private Cloud: You own the cloud infrastructure entirely or the cloud provider provides you with a unique service. For this, you must host your apps either on on-premise servers or on a dedicated server offered by the cloud provider.
Hybrid Cloud: This model is a hybrid of the private cloud and the public cloud. It involves using dedicated servers to process confidential, sensitive data and public cloud capabilities to host public-facing applications.
18. What is the difference between Azure and AWS?
Azure and AWS are two of the most popular cloud computing platforms available today. While they offer many similar services, there are some key differences between them:
Market presence: AWS has been around since 2006 and enjoys the largest market share, while Azure, launched in 2010, is the second largest. Azure is growing at a faster rate as it benefits from its integration with other Microsoft products.
Service offerings: While both offer a comprehensive set of services, AWS provides a slightly wider range of features and options. However, Azure is catching up quickly, constantly expanding its range of services.
Integration with other products: Azure has better integration with other Microsoft products like Office 365, Dynamics 365, and Power BI. This makes it appealing to organizations already invested in Microsoft technologies. AWS, on the other hand, is more focused on open source and has a broader ecosystem of third-party integrations.
Hybrid cloud support: Azure has a stronger emphasis on hybrid cloud solutions with services like Azure Stack that enable organizations to build and deploy hybrid applications consistently across on-premises and cloud environments. AWS also supports hybrid cloud but primarily focuses on cloud-native applications.
Pricing: Both providers offer a pay-as-you-go pricing model, but the specific costs can vary depending on the services and features required. AWS tends to have more granular pricing options with per-second billing and savings plans, while Azure offers discounts and extended contract periods for enterprises.
User interface and usability: Azure is known for a more user-friendly portal interface, while AWS Management Console is more advanced and offers more customization options. AWS users often utilize third-party tools or command-line interfaces for usability improvements.
19. What are Azure Resource Manager templates?
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates are JSON files that specify the configuration and infrastructure of a project within the Azure deployment. They help with the creation, deployment, and management of Azure resources as a group.
ARM templates can be used for defining and deploying a range of Azure resources, such as virtual machines and networks, databases, web apps, and storage accounts. Templates can be written using JSON syntax and can be stored in source control which makes it easy to version, share, and update templates as needed.
20. What do you understand by Azure Pipelines?
Azure Pipelines is a cloud-based continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) service from Microsoft. It lets users build, test, and deploy their applications to a destination of their choice, and supports all major languages and projects.
With Azure Pipelines, developers can create automated workflows that run tests, build and package applications, and deploy them to multiple environments, including on-premises servers, virtual machines, and cloud services.
21. How is Azure DevTest Labs helpful in reliable testing?
Azure DevTest Labs enables developers to quickly create Azure environments for the purpose of deploying and testing their applications. The service offers easy provisioning of Linux and Windows machines in Labs via reusable templates which minimizes the cost of the entire process.
It also provides integration with CI/CD pipelines, resource management, and self-service capabilities to developers and testers. It provides a reliable and efficient way to manage testing environments and implement robust testing.
22. What is the Azure Functions premium plan?
The Azure Functions premium plan is a premium offering from Microsoft that provides all the features included in the standard consumption plan in addition to others like enhanced performance, VNet access, and no cold start, among others.
The premium plan also offers virtual network integration or connectivity by allowing applications to get secure access to resources on the virtual network. Besides this, you also get longer runtime durations, premium instance sizes, and higher-density app allocation.
23. What is the Azure Monitor used for?
Azure Monitor is a complete monitoring solution that is used for the collection, analysis, and telemetry response to applications from the cloud and on-premise platforms.
It helps collect and aggregate the data from different layers and components of the system to a common platform. Azure Monitor is generally used to optimize the performance and availability of applications and services on the cloud.
24. Explain the Azure Site Recovery feature.
Azure Site Recovery is a disaster recovery solution that helps organizations protect and recover their workload in situations of outage or disruption. It provides a simple, automated, and scalable solution for replicating and recovering virtual machines, physical servers, and applications to Azure or other data centers.
Recovery processes, deploy replication, and failover are some of the methods used by Azure Site Recovery to keep applications running in case of planned and unplanned outages.
25. What does NSG mean?
NSG is an abbreviation for Network Security Group, which contains a set of ACL (Access Control List) rules that allow or deny network traffic to subnets, NICs (Network Interface Cards) linked to a subnet, or both. When NSG is connected to a subnet, the ACL rules apply to all virtual machines in that subnet.
26. What is Azure ExpressRoute?
Azure ExpressRoute is a dedicated service from Azure that helps establish private and exclusive connections from an on-premises network to Azure data centers using a connectivity provider.
When using ExpressRoute, connections are not routed through public networks. Instead, a dedicated, private network is used to provide users with faster speeds, higher reliability, improved security, and consistent latency.
27. What do you understand by Azure CDN?
Azure CDN stands for content delivery network. It is a globally distributed server network for the efficient delivery of web content to end-users. It enables organizations to deliver high-bandwidth content to users around the world with low latency and high availability.
Azure CDN provides a globally distributed network of servers with content cached on edge servers, close to end-users, thereby reducing the distance and time required to deliver the content.
28. What do you understand by Azure Scheduler?
Azure Scheduler enables you to perform background trigger events or operations such as calling HTTP/S endpoints or presenting a message on the queue on any schedule.
With Azure Scheduler, tasks in the cloud call services within and outside of Azure to perform on-demand jobs that are frequently repeated on a regular schedule or to start those jobs at a future set date.
29. What is Azure AD Connect primarily used for?
Azure AD Connect is a useful tool to connect on-premises applications for accomplishing and meeting hybrid identity goals. Azure AD Connect allows you to integrate on-premises identity infrastructure with Azure AD, which is the cloud-based identity and access management service provided by Microsoft. By doing so, you can use your existing Active Directory credentials to access cloud resources like Office 365, Azure, and other Microsoft online services.
30. What is the role of Azure Traffic Manager?
Azure Traffic Manager is a traffic load balancer based on DNS. It is used to route incoming traffic to multiple end-points across various Azure regions globally. It offers increased responsiveness and high availability to your public endpoint through optimized scaling of traffic.
Traffic Manager uses DNS to direct client requests to the best endpoint based on the routing method you choose. You can also use it to route traffic to specific endpoints based on factors like performance, cost, or regulatory compliance requirements.
31. Explain Azure Backup.
Azure Backup is a cloud-based backup and recovery solution that enables you to backup and restore data for applications, virtual machines, and files. You can automatically allocate and manage the backup storage. The pay-as-you-use model helps with cost efficiency.
Azure Backup can be used for various scenarios, including on-premise servers, Azure virtual machines, SQL databases, and Azure files.
Wrapping up
This comprehensive collection of the latest and the most popular Azure interview questions can help you evaluate candidates for their technical proficiency in Azure. As a recruiting manager, if you want to simplify the hiring process, you can join Turing to hire the world’s best Azure developers, rigorously vetted by AI, on the cloud.
If you are a developer, this set of questions can help you prepare for your interview and get a good understanding of the different Azure concepts. However, it is recommended that you also work on your soft skills such as communication, problem-solving, and collaboration skills to crack the interview and blend seamlessly with the team. You can apply to the latest Azure jobs at Turing and enjoy a range of benefits including high-paying jobs, career growth, and developer success support.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber Azure developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.