Vue.js
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is Vue.js, and what are its key features?
Vue.js, often referred to as Vue, is a popular open-source JavaScript framework used for building user interfaces and web applications. Created by Evan You and first released in 2014, Vue.js has gained significant traction in the web development community due to its simplicity, flexibility, and impressive performance. Here are some key features and characteristics of Vue.js:
Progressive Framework: One of Vue.js's standout features is its progressive nature. It allows developers to use as much or as little of the framework as they need. You can gradually introduce Vue.js into an existing project, making it versatile and easy to adopt.
Declarative Rendering: Vue.js uses a declarative approach to building UIs. Developers describe the desired outcome of the user interface, and Vue.js takes care of the underlying logic and updates the DOM (Document Object Model) accordingly. This makes the code more intuitive and easier to understand.
Component-Based Architecture: Vue.js is built around a component-based architecture. Components are self-contained, reusable building blocks that can be composed to create complex user interfaces. This promotes code reusability and maintainability.
Virtual DOM: Vue.js employs a Virtual DOM (Virtual Document Object Model) to optimize DOM manipulation. Instead of directly updating the real DOM, Vue.js makes changes to a virtual representation first and then efficiently updates the actual DOM only where necessary, reducing unnecessary re-rendering and enhancing performance.
Two-Way Data Binding: Vue.js provides two-way data binding out of the box. This means that changes to the model (data) are automatically reflected in the view (UI), and vice versa. This simplifies data synchronization between components.
2. How do you create a new Vue instance?
To create a new Vue instance, you need to use the Vue constructor function. Here's an example:
const app = new Vue({ // Options and configuration go here });
3. Explain the Vue instance lifecycle hooks.
Vue instance lifecycle hooks are specific methods that allow you to perform actions at different stages of a component's lifecycle. The main lifecycle hooks are beforeCreate, created, beforeMount, mounted,beforeUpdate, updated, beforeDestroy, and destroyed.
They enable you to interact with data, perform computations, or manipulate the DOM at various points during the component's existence.
4. What is data binding in Vue.js?
Data binding in Vue.js is the automatic synchronization of data between the model and the view. It allows changes to the application state to be reflected in the UI and vice versa, without manual intervention.
Vue supports one-way data binding (v-bind or : ) and two-way data binding (v-model) to streamline the process of updating the data and the UI.
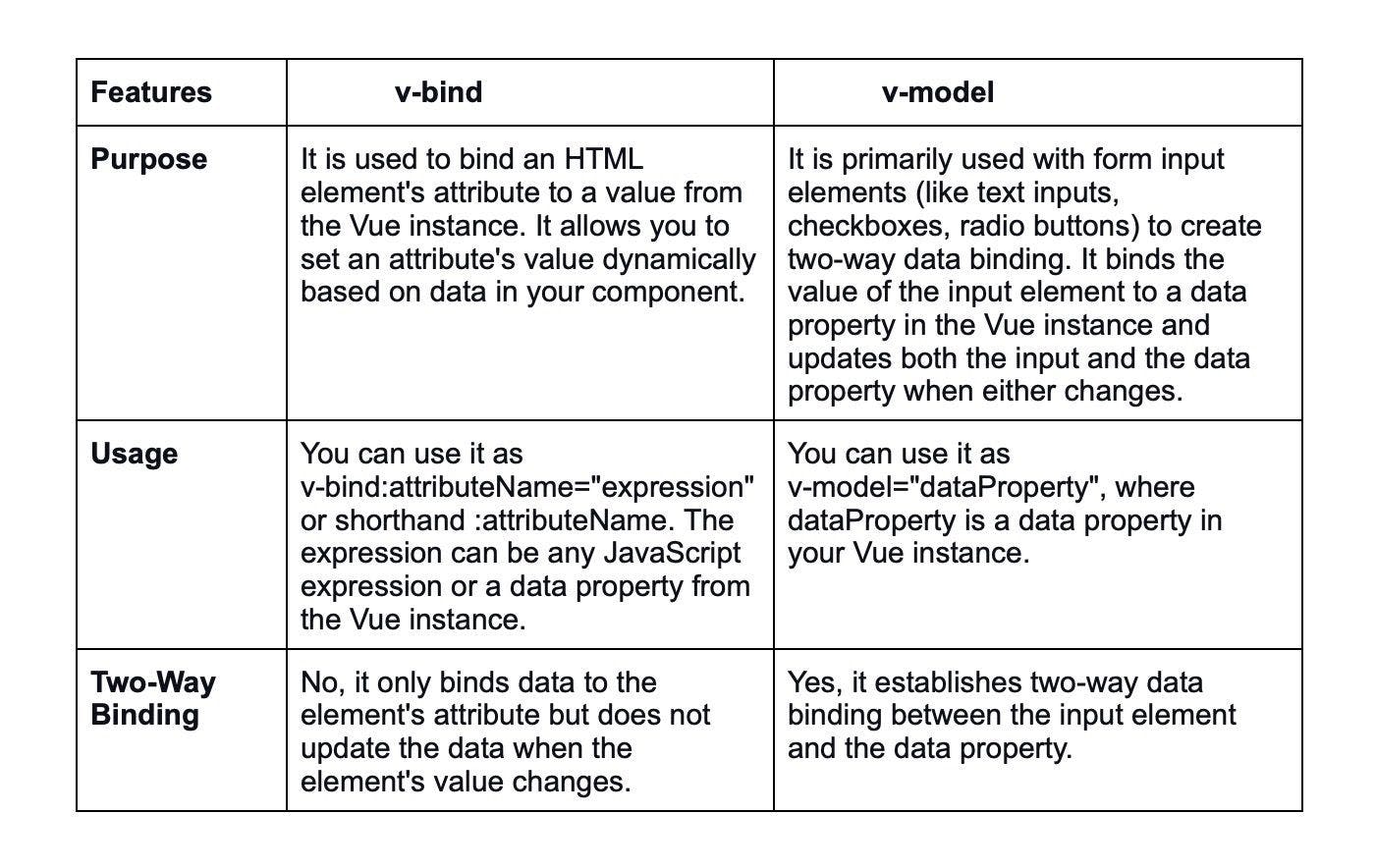
5. What is the difference between v-bind and v-model directives?
v-bind and v-model are both directives in Vue.js used to interact with data and update elements in the DOM, but they serve different purposes:
6. How do you handle user input and events in Vue.js?
To handle user input and events in Vue.js, you can use the v-on directive (or @ shorthand). By binding event listeners to methods, you can respond to user interactions, such as button clicks, input changes, or keyboard events.
7. What is the purpose of computed properties in Vue.js?
Computed properties in Vue.js are used to calculate and cache derived data from the component's reactive data. They help avoid unnecessary recalculations by updating only when their dependencies change. Computed properties are often used for complex calculations or data transformations.
8. How can you conditionally render elements in Vue.js?
You can conditionally render elements in Vue.js using the v-if, v-else, and v-else-if directives. These directives allow you to control the rendering of elements based on certain conditions or expressions.
9. How do you loop through an array in Vue.js using v-for?
To loop through an array in Vue.js, you can use the v-for directive. It allows you to iterate over an array and render elements for each item in the array.
Here's an example:

10. What is the significance of the "key" attribute when using v-for?
The "key" attribute in v-for is essential for efficient list rendering and helps Vue identify each rendered item uniquely. It aids in maintaining the component's state and reusing elements instead of recreating them when the list changes, improving performance.
11. Explain directives in Vue.js.
This is an important Vue.js interview question. The directive is a piece of markup that tells the library what to do with a certain DOM element. Vue.js comes with a number of built-in directives, such as v-bind and v-model. You can also make your own directions.
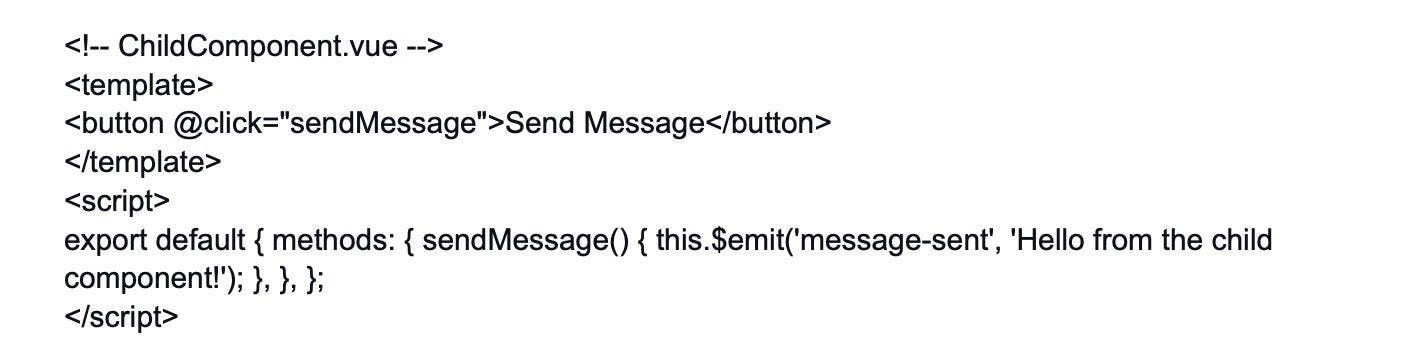
12. How can you share the data between components in Vue.js application?
Data flow is important for transferring information between components.
Parent Component to Child - 'Props' is used to send data from a parent component to a child component. Props are custom attributes that you may register on a component, and when a value is supplied to those props attributes, that component instance becomes a property. As a result, all modifications made by the parent component are reflected in the prop attribute of the child component.
To handle this problem, Vue instances provide the notion of events. Child Component to Parent - Some scenarios may necessitate communication back to the parent component, hence Vue instances provide the concept of events to solve this case.
The parent component can use 'v-on' to listen to any event on the child component, and the child component can use the $emit method to emit any event.
Data Sharing Across Components - In some cases, data sharing across all components may be essential. Vuex overcomes this challenge by establishing a centralized data store that is accessible to all components.
13. How do you handle conditional rendering using the "v-if" and "v-else" directives?
You can use the v-if and v-else directives to handle conditional rendering in Vue.js. When the condition specified in v-if evaluates to true, the associated element is rendered; otherwise, if the condition is false, the element associated with v-else is rendered.
14. What are the Jest and Mocha in Vue CLI?
This is a rather popular Vue.js interview question. Jest and Mocha are built-in unit testing tools in the Vue CLI. Jest is a Facebook-developed test runner. It provides a unit-testing solution that is battery-powered. To run Jest tests, use the Vue CLI plugin 'cli-plugin-unit-jest'.
Mocha is a JavaScript-based test framework for asynchronous testing that works on Node.js and in browsers. It includes a built-in webpack precompiler.
15. What is the usage of $parent?
In the child component, $parent is used to retrieve the parent component instance. It's more difficult to test and debug the program, and you can't figure out where the mutation comes from. Vue also has a $child function that returns a child component instance, similar to $parent.
16. What is a Key?
This is one of the most asked Vue.js interview questions. In Vue, the key attribute is used as a clue for the virtual DOM technique to distinguish VNodes when creating a new node list from an existing one.
If the 'key' attribute is not utilized, Vue utilizes an algorithm that tries to reuse elements of the same type and reduces element movement. The elements with the 'key' property, on the other hand, will be reordered and the elements without it will be eliminated. It's similar to AngularJS's $index. It's most commonly used in conjunction with the 'v-for' directive.
17. Explain the significance of the "ref" attribute in Vue.js and when to use it.
The "ref" attribute in Vue.js is used to give components or HTML elements a unique reference, allowing you to access them directly from the parent component using this.$refs. It is often used when you need to interact with child components or access specific elements in the DOM directly.
18. What is the "v-once" directive, and how does it differ from other directives?
The "v-once" directive is used to render an element or component only once, and it prevents it from being updated even if its data changes. Unlike other directives, which re-render elements when data changes, "v-once" is useful when you have static content that doesn't need to be re-evaluated.
19. How do you handle two-way data binding in Vue.js using the "v-model" directive?
The "v-model" directive provides two-way data binding in Vue.js. It allows you to bind form inputs (like text fields, checkboxes, or radio buttons) to a data property. Changes in the input elements update the data property, and changes in the data property are reflected in the input elements.
20. Explain the component Prop.
Data is passed from the parent component to the child component using Component Prop. A component can have as many props as it wants. The prop is a custom attribute that becomes a property on the component instance when a value is supplied to it.
From parent to child component, a component Prop forms a one-way down binding. When the parent property changes, it affects the child, but not the other way around. As a result, when the Parent component is modified, all child components are updated as well. As a result, you won't have to worry about mutating the prop in the child component.
21. What is the One-Way Data Flow in Vue.js?
This is a popular Vue.js interview question. All Props work in one direction, which means data flows from parent to kid. When a modification is made to a parent property, the child property is automatically updated, but not the other way around. It prohibits a child from changing the state of the parent property, which can make your application's data flow more difficult to comprehend.
22. Explain the concept of event modifiers in Vue.js and provide some examples.
Event modifiers in Vue.js are special postfixes denoted by a dot that allows you to modify the behavior of event handlers. For example, .stop prevents event propagation, .prevent prevents the default behavior of the event, and .once ensures that the event listener will be triggered only once.
Example:

23. What is the single file component?
SFCs, or single file components, are similar to other components in that they are self-contained in their own files. The following are some of the benefits of SFCs.
- Global Definitions - This refers to the fact that all SFCs are registered globally and given unique names.
- Strong Templates - Instead of using a single template property like other components, you can easily create template code in SFCs.
- CSS Support – SFCs allow you to apply CSS to the component itself.
- Support for preprocessors – preprocessors like babel, SAAS, and others can be simply used in SFCs.
24. How can you handle keyboard events in Vue.js applications?
You can handle keyboard events in Vue.js by using the v-on directive with appropriate event names, such as @keydown, @keyup, or @keypress. You can then call a method in response to these events to handle user keyboard input.
25. What is the purpose of the "v-html" directive, and what are its potential security risks?
The "v-html" directive allows you to render HTML content dynamically from your data. However, it comes with potential security risks, as it can lead to code injection attacks if the HTML content is not properly sanitized. It is recommended to use it only with trusted content or combined with proper sanitization methods.
26. What is the Vue CLI, and why is it useful for Vue.js development?
The Vue CLI is a command-line tool used to scaffold Vue.js projects quickly and efficiently. Being one of the popularly used Vue tools, it provides a set of preset configurations and project templates, allowing developers to start their projects with best practices and modern development tools, such as Webpack and Babel, pre-configured.
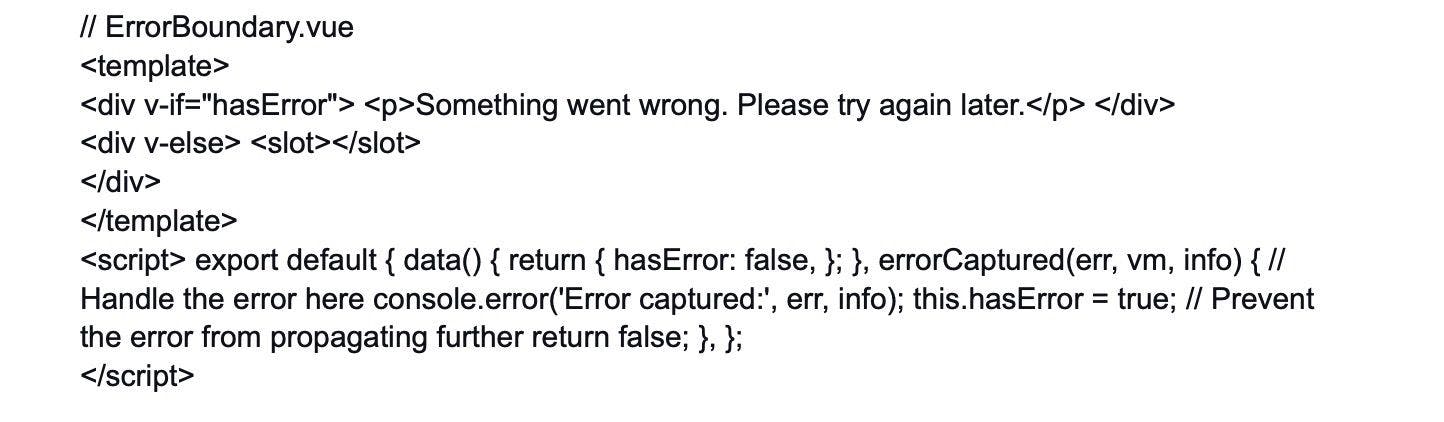
27. How do you handle errors and exceptions in Vue.js applications?
In Vue.js, you can use the errorCaptured lifecycle hook at the component level to handle errors that occur within a component and its children. Additionally, you can use global error handlers, like Vue.config.errorHandler, to handle errors across the entire application.
28. Explain the concept of watchers in Vue.js and when to use them.
Watchers in Vue.js allow you to react to changes in data properties and perform specific actions when these properties change. Watchers are particularly useful when you need to perform asynchronous operations or complex logic based on data changes.
29. How can you render raw HTML in Vue.js templates?
To render raw HTML in Vue.js templates, you can use the "v-html" directive. However, be cautious when using this directive with user-generated or untrusted content to prevent security vulnerabilities.
30. How do you bind CSS styles dynamically in Vue.js using the "v-bind" directive?
To bind CSS styles dynamically in Vue.js, you can use the "v-bind" directive (or : ) with the style attribute. For example:
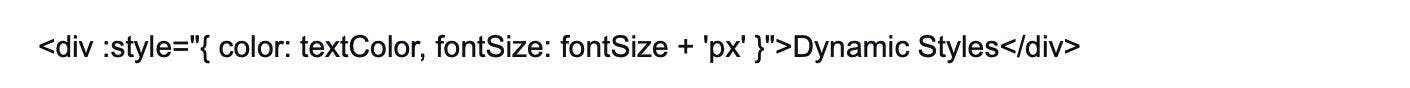
In this example, textColor and fontSize are data properties that can be changed dynamically.
31. Explain the use of filters in Vue.js. Are filters recommended in modern Vue.js applications?
Filters in Vue.js are used to format and transform text when displaying it in the template. However, filters have been deprecated in Vue 2.x and are not recommended for use in modern Vue.js applications. Instead, it's recommended to use computed properties or methods to achieve similar functionality.
32. What is the purpose of the "v-pre" directive in Vue.js templates?
The "v-pre" directive tells Vue to skip compilation for a specific element and its children. It is useful when you have complex templates with a lot of data bindings, and you want to improve performance by skipping unnecessary compilation for certain parts of the template.
33. How can you handle and manage the local component state in Vue.js?
You can handle the local component state in Vue.js by defining a "data" function within your component and returning an object with the desired properties. These properties can then be accessed and modified within the component's methods, computed properties, and template.
34. What is the Vue.js Devtools, and how can it assist in debugging Vue.js applications?
The Vue.js Devtools is a browser extension that allows developers to inspect and debug Vue.js applications. It provides a detailed view of the component hierarchy, current state, props, data, and events. It also allows you to time-travel and inspect changes to the application's state.
35. How can you handle conditional classes in Vue.js using the "v-bind" directive?
You can handle conditional classes in Vue.js using the "v-bind" directive (or :) with an object syntax. By binding an object of class names and their corresponding conditions, you can dynamically apply or remove classes based on specific conditions.
36. Explain the use of the "v-once" directive and its implications for rendering.
The "v-once" directive is used to render an element or component only once, and it prevents it from being updated even if its data changes. It can be useful for static content that doesn't change, as it optimizes rendering and improves performance. However, any dynamic content inside the "v-once" block will not update when the underlying data changes.
37. How do you handle form submissions in Vue.js applications?
To handle form submissions in Vue.js applications, you can use the v-on directive with the "submit" event. By binding the form submission to a method, you can access form data and perform actions like data validation or making API calls.
38. What are the differences between "v-show" and "v-if" directives in terms of rendering behavior?
The "v-show" directive toggles the element's visibility by modifying the "display" CSS property. The element remains in the DOM, but it's not visible when the condition is false. In contrast, the "v-if" directive completely adds or removes the element from the DOM based on the condition.
39. How do you create custom events in Vue.js?
To create custom events in Vue.js, you can use the $emit method in the child component to send a specific event along with optional data. Then, in the parent component, you use the v-on directive (or @ shorthand) to listen to the custom event and trigger a method accordingly.
40. Explain the concept of template ref and provide a scenario where you would use it.
Template refs allow you to access child components or DOM elements directly from the parent component. This is useful in scenarios where you need to call methods or access properties of child components programmatically. For example, using a ref to access a form element and trigger its validation method.
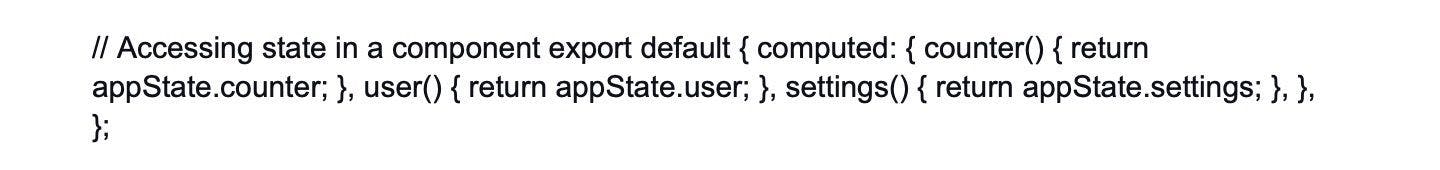
41. How do you manage the application state without using Vuex?
While Vuex is a popular choice for state management, you can manage the application state without Vuex by leveraging Vue's reactivity system and passing down props between parent and child components.
However, for large-scale applications, Vuex simplifies state management and ensures a more organized and centralized approach.
Wrapping up
Vue.js is a potent and adaptable framework that is revolutionizing the web development industry. We hope that this thorough list of Vue.js interview questions and answers has been a beneficial resource for both prospective applicants and hiring managers.
Vue.js developers hold the key to unlocking innovation and building cutting-edge solutions for your company. In this era of fast pace development, the right talent with best skill-set can propelt yout towards the best outcome.
Are you ready to revolutionize your AI-powered IT service company with Vue.js expertise? Don't wait; start hiring top Vue.js developers today and stay ahead of the competition!
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber Vue.js developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.