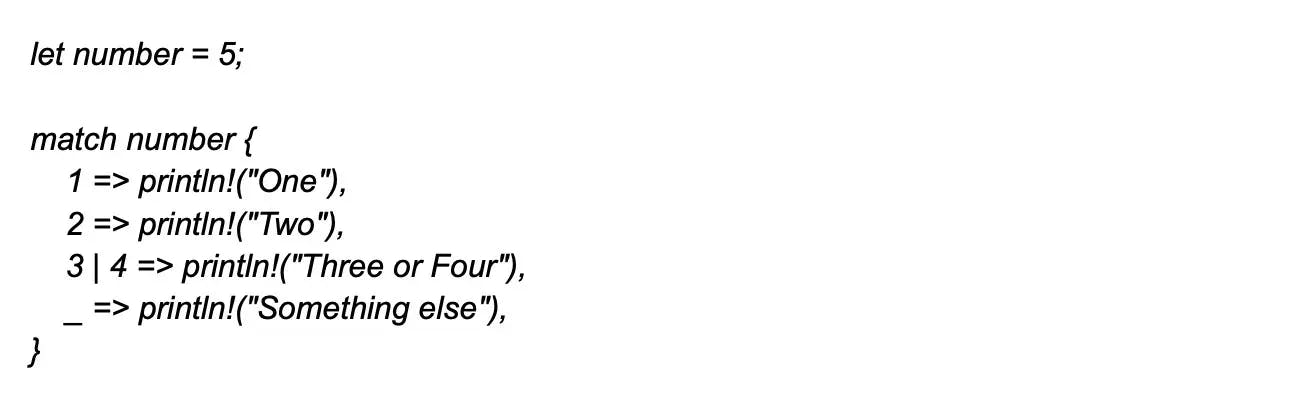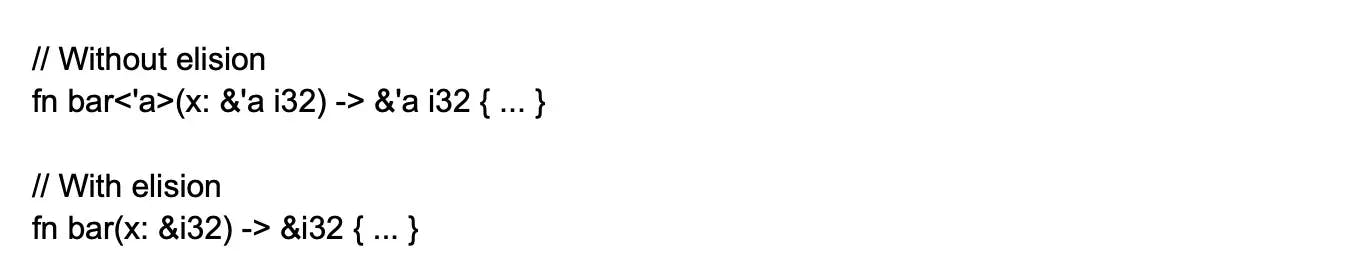Rust
Basic Interview Q&A
1. How would you describe Rust programming language?
Rust is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm programming language offering high performance and concurrency. Rust is known for its unique ownership and borrowing system, which allows for memory management without needing a garbage collector.
This system ensures that memory is never accessed incorrectly or freed too early, eliminating many common runtime errors and making Rust programs more reliable and secure.
2. What are the key features of Rust?
Rust offers several features that make it a popular choice for developers. Some of its prominent features include:
High performance: Rust is designed to be highly efficient and fast, with low-level control over system resources, thus ensuring excellent performance.
Concurrency: Rust supports concurrency and parallel execution with features such as threads and message passing.
Memory safety: Rust has a unique ownership and borrowing system that ensures memory safety without significant runtime overheads.
Zero cost abstractions: The abstractions used in Rust don’t incur any runtime cost due to code optimization implemented by the compiler.
Macros: Rust offers a robust macro system that enables optimized code generation and meta programming.
Cargo integration: Rust provides a built-in package manager known as Cargo, which helps to manage dependencies and easily build projects.
Error messaging: Error messaging: Rust has improved error messages compared to many other programming languages, including C++. It provides clear, concise, and detailed explanations of errors with proper formatting, colors, and highlighted misspellings, aiding developers in identifying and fixing the issues efficiently.
3. Describe ownership in Rust.
In Rust, ownership is a fundamental concept that defines and governs how the memory is managed in a Rust program. It is a mechanism that allows Rust to implement memory safety without needing a garbage collector.
Every value, in Rust, has an owner, the variable that holds the value. When the owner goes out of scope, the value is dropped, which frees the associated memory.
4. Which platforms are supported by Rust?
There are various platforms supported by Rust, including the following:
- Linux
- macOS
- Windows
- iOS
- Android
- FreeBSD
- NetBSD
- OpenBSD
- Solaris
- WebAssembly
Rust has strong cross-compiling support, allowing developers to build applications for multiple target platforms from a single development environment.
5. What are the steps for installing Rust?
The steps to install Rust are as follows:
- Open a terminal (on Linux or macOS) or Command Prompt (on Windows).
- Run the following command to download the Rust installation script:

- Alternatively, download and run the rustup-init.exe file from the official Rust website for Windows.
- Once the script has finished downloading, it will prompt you to begin the installation process. Press "1" to proceed with the default installation, which installs Rust and its associated tools.
- The script will then download and install the necessary components. This may take a few minutes.
- Rust will be ready to use once the installation is complete.
Now you can start using Rust to build your projects.
6. How to declare global variables in Rust?
In Rust, you can declare a global variable using the static keyword. The static keyword declares a global variable with a static lifetime, which means that it exists for the entire duration of the program's execution.
To declare a global variable, you need to specify the type, and it must have a constant expression for initialization. Additionally, since global variables can be accessed from multiple threads, one must ensure to handle synchronization when using mutable global variables.
7. What are the limitations of Rust?
Here are some major limitations associated with the Rust programming language:
Learning Curve: Rust can be difficult, especially for those new to programming or unfamiliar with systems programming languages. It has a steep learning curve, and its syntax can be complex and unfamiliar to many developers.
Memory Management: While Rust's ownership and borrowing system is designed to prevent memory-related bugs, it can also be quite restrictive, requiring developers to manage memory usage and ownership of variables carefully.
Slow Compilation: Rust is known for having slow compilation times, especially compared to other modern programming languages. This can frustrate developers who need to iterate quickly during the development process.
Limited Libraries: Rust is still a relatively new language, and as a result, its library ecosystem is not as mature as that of other languages like Python or JavaScript. This can make it difficult to find and use third-party libraries and frameworks.
8. How to write a GUI application in Rust?
To write a GUI (Graphical User Interface) application in Rust, you can use one of several available GUI libraries and frameworks. Here are some popular options:
Cocoa: Cocoa is a macOS native UI framework (not a Rust library) that can be accessed using the cocoa-rs Rust bindings. It allows you to create native macOS applications. However, be aware that using Cocoa directly will be platform-specific and won't be cross-platform.
ImGui: ImGui (also known as Dear ImGui) is a bloat-free graphical user interface library for C++. It is popular for creating graphical interfaces for game development, tools, and applications.
GTK: Gtk-rs is a set of bindings for the GTK library, which is a popular GUI library for creating native-looking and highly customizable interfaces.
Gyscos: gyscos is a TUI (Text User Interface) library for Rust. It builds interfaces in the terminal using different backends (like termion, ncurses)
IUP: IUP (Interface User Portable) is a GUI library initially developed in C to provide a minimalistic and easy-to-use interface. IUP has Rust bindings called iup-rust, which allows you to use IUP for building GUI applications in Rust.
9. What are the ownership model rules in Rust?
The ownership model rules in Rust ensure memory safety, and these rules are as follows:
- Each value in Rust has a single owner.
- When the owner goes out of scope, the value is dropped.
- When a value is moved from one variable to another, the original variable can no longer access the value.
- Rust's borrowing system allows temporary access to a value without taking ownership.
10. Is it possible to create an operating system entirely in Rust?
Yes, you can write a whole operating system in Rust. Rust is now the primary programming language in several recently launched operating systems. Developers use Rust to create various new software applications, including game engines, operating systems, file systems, browser components, and virtual reality simulation engines.
11. What is borrowing in Rust?
In Rust, borrowing refers to an activity where a program can get temporary access to a resource, such as a variable, without assuming permanent ownership of the resource.
Borrowing allows the code to access the variable value without needing ownership of the variable. This ensures that various parts of a program can access resources without needing a transfer of ownership or creating new copies.
12. What is a lifetime in Rust?
In Rust, lifetime is a construct that describes the relationships between data references in memory and data lifetime. The Rust compiler uses lifetime to understand and track the length of reference validity.
It is like a label attached to a reference that indicates how long the reference is valid and thus can be used for accessing the data it refers to.
13. What is a module in Rust?
Rust offers a robust module system to organize and manage the code's visibility. A module has several items, including functions, constants, enums, traits, and structs, into separate units. Modules provide namespaces for your items, helping avoid naming conflicts and making it easier to reason about your code organization.You can create a module using the mod keyword followed by the module's name and a block where you can define items inside the module.
14. What is pattern matching in Rust?
Pattern matching is a feature that enables developers to specify patterns and check them against value structure. It provides a concise way to match the patterns in data and then execute the code based on the match. In Rust, pattern matching is done using the ‘match’ expression.
15. Is Rust safe in comparison to C and C++?
The most significant advantage of Rust over C is its emphasis on writing safe code. Rust was created, with memory safety being one of its top priorities. Rust provides several features which make it difficult to write unsafe code.
C and C++ offer greater control and flexibility on memory management and other low-level operations, which can adversely affect safety. Rust is a safer language in comparison to C and C++.
16. What is a reference in Rust?
A reference in Rust is essentially a pointer that refers to the value without owning it. References allow parent functions to retain the original variable scope while allowing the child function to use it. This means that multiple parts of the program can access the same data without owning it or making copies.
17. What are the types of references in Rust?
There are two types of references in Rust: immutable references and mutable references.
Immutable references: These are read-only references that allow you to borrow an immutable view of a value. When you have an immutable reference to a value, you cannot mutate the value through that reference. Immutable references are created using the & symbol followed by the value you want to borrow.
Mutable references: These are references that allow you to borrow a mutable view of a value. When you have a mutable reference to a value, you can mutate the value through that reference. Mutable references are created using the &mut keyword followed by the value you want to borrow.
18. What's the connection between Rust and the reusable codes it generates?
In Rust, the compiler enforces the ownership model, meaning there are no unmanaged pointers or memory leaks. This makes writing reusable code incredibly easier and more efficient.
Also, Rust’s package manager, Cargo, makes code sharing and reusability very simple. Rust has many libraries and packages, making it easy for developers to write modular and reusable code and leverage existing code to accelerate development.
19. What is the unwrap () method in Rust?
unwrap() is a method provided by Rust programming language's standard library that can extract the value inside an Option or Result type while also propagating any potential errors that might have occurred.
In Rust, the ‘Option’ and ‘Result’ types are used extensively to handle situations where a value may or may not be present or an operation can fail due to some error. To access the value inside an ‘Option’ or ‘Result,’ you need to use one of several methods provided by these types, such as unwrap(), expect(), map(), match, etc.
20. What is a struct in Rust?
Struct, also known as Structure, is a composite data type that allows you to group together related values under a single name. Structs can represent concepts or objects in your program, allowing you to structure your data in a more organized way. They are similar to structures in C, classes in C++/Java, or records in Pascal, while not having an inherent behavior like classes in object-oriented languages.
21. What is the difference between an option and a result in Rust?
In Rust, an option and a result are both types that represent the possibility of having an error or a successful value. However, some differences between them are:
- An ‘Option’ represents the computational value that may or may not be present. For instance, it is used when there is a possibility that the function might not return a value while looking for an item within a collection. The option can either contain ‘Some (value)’ or ‘none,’ and it is generally used to avoid null pointer errors.
- A ‘Result’ represents an operational result, which can either be a success or a failure with an associated error value (E) if it is a failure. The ‘result’ type is usually used in cases where a function might fail for several reasons, and thus the error cases can be handled in a structured way.
22. What is a procedural macro in Rust?
In Rust, a procedural macro is a type of macro that allows you to define custom syntax extensions that can be used in your code. Procedural macros are implemented as Rust functions that take in Rust code as input, manipulate it in some way, and then generate output with a new Rust code. Procedural macros are used to generate code at compile time.
23. What is a data race in Rust?
A race condition in Rust can be defined as multiple threads (usually more than 2) trying to access the same data or memory location at the same time concurrently, where at least one access is a write operation. This can lead to undefined behavior like data corruption, program crashes, or security vulnerabilities.
24. How does Rust ensure memory safety?
Rust ensures memory safety through two primary approaches:
Strict type system: Rust's type system helps prevent memory safety issues by ensuring that types are checked at compile time. This means the compiler can catch many errors before the code is run, such as trying to access a value that has already been moved or borrowed.
Ownership and borrowing system: In Rust, every value has an owner responsible for managing the memory allocated to that value. Rust ensures that there is only one owner for a value at a time, preventing issues such as dangling pointers or use-after-free bugs. In addition to ownership, Rust also employs borrowing. Borrowing allows a function or method to temporarily borrow a value owned by another part of the program.
25. What is cargo.lock file in Rust?
Cargo.lock contains information related to the dependencies of a Rust project, such as transitive dependencies. The objective of this file is to ensure that anyone building a new project will use the same dependencies as the last version of the project to avoid dependency conflicts and ensure reusable builds.
26. What is an enum in Rust?
In Rust, an enum is a type that enables developers to define a set of named values or data. These values can have several variants, and they can also have additional or optional data.
Enums can be useful in Rust for representing data that can take on a limited set of values, like the days of the week or the options for a user interface. They can also define custom error types or other complex data structures.
27. What is a conditional compilation in Rust?
In Rust, conditional compilation is a feature that enables developers to compile specific parts of the code using predefined conditions selectively. This feature is usually used for developing platform-specific code or creating functionality for specific build configurations.
In Rust, conditional compilation is achieved using the #[cfg] attribute. This attribute can specify a condition determining whether a particular block of code should be included in the final compiled binary.
28. What is a build script?
A build script is a special source file in Rust, and this file is executed during the build process of a project. A build script performs several tasks, including the following:
- Generating code
- Setting environment variables
- Compiling external dependencies
- Configuring build options
29. What is an iterator in Rust?
In Rust, the iterator is a process that provides a sequence of values that can be iterated using iterator methods such as ‘for loop.’ Iterators help to implement looping. To use an iterator in Rust, you typically create an instance of a type that implements the Iterator trait and then use it in a loop or with other iterator methods.
30. What is a channel in Rust?
A channel is a mechanism for communication and passing messages between two concurrent execution threads. A channel consists of a sender and a receiver, and there is unidirectional information flow in one direction from the sender to the receiver. Channels in Rust are implemented using the std::sync::mpsc module.
31. What do you know about cargo.toml file in Rust?
Cargo.toml is a configuration file used in the package manager used by Rust named Cargo. This file contains metadata and specifies information about the project name, version, build settings, and dependencies.
This file is written in ‘TOML’ format, i.e., Tom’s Obvious Minimal Language, which is a simple configuration language. By using Cargo.toml, you can easily manage your project's dependencies and build settings, making it easier to share and collaborate with others.
32. What is a declarative macro in Rust?
In Rust, a declarative macro allows you to define a pattern that will be matched against the input code and then generate new code based on that pattern. Declarative macros are defined using the macro_rules! macro.
The macro_rules! the macro takes as input a set of rules that define the pattern to match and the code to generate and generates code that implements the macro.
33. What do you understand by function pointer?
A function pointer is a type that represents a pointer to the function whose identity might be unknown at compile time. It enables developers to store a reference to a specific function that can be called another time in the code.
Function pointers are helpful when you have to pass a function as an argument to another function or when you are storing a function in a data structure. In Rust, you can define a function pointer using the fn keyword and the *const or *mut pointer syntax.
34. Explain Tuple in Rust.
A tuple is a collection of different types of values. It is similar to an array, but unlike arrays, a tuple can contain values of different types. A tuple is constructed using parentheses, and the values within that are separated by commas.
Example:
let my_tuple = (10, "hello", true);
35. Explain the match statement.
The match statement is a control flow operator that provides a powerful mechanism to transfer control to a specific code block based on the matching patterns of the variables. It enables you to compare a value across a series of patterns and then execute the relevant block of code based on pattern matches.
When the match statement is executed, Rust will try each pattern in order and execute the code associated with the first pattern that matches the value.
Wrapping up
So, this comprehensive list of the latest and the most popular Rust interview questions in 2023, can help you evaluate candidates for their technical proficiency in Rust. As a recruiting manager, if you want to simplify the hiring process, you can join Turing to hire the world’s best Rust developers, rigorously vetted by AI, on the cloud.
If you are a developer, this set of questions can help you prepare for your interview and get a good understanding of the different Rust concepts. However, it is recommended that you also work on your soft skills such as communication, problem-solving, and collaboration skills to crack the interview and blend seamlessly with the team. You can apply to the latest Rust jobs at Turing and enjoy a range of benefits including high-paying jobs, career growth, and developer success support.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber Rust developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.