C++
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is C++?
C++ is a powerful imperative, general-purpose programming language. It was developed as an extension of the C programming language and provides additional features like object-oriented programming and templates.
C++ is used to develop various applications including operating systems, games, and high-performance software. Its syntax is similar to C which makes it easy for C programmers to transition to C++.
2. What is a namespace in C++?
In C++, a namespace is a way to group related code under a single name. It helps in organizing code and prevents naming conflicts. By using namespaces, you can avoid clashes between function names or variable names that are used in different parts of a program or in external libraries.
Namespaces provide a way to logically separate code and improve code readability and maintainability.
The code is:

3. What is operator overloading in C++?
Operator overloading in C++ allows an operator to have different behaviors depending on the types of operands used. It enables operators like +, -, * to perform custom operations on user-defined classes.
For example, you can define what happens when you add two objects of a class. This feature helps make code more expressive and readable by allowing operators to work intuitively with user-defined types.
4. How to learn C++?
Learning C++ can seem daunting, but there are effective ways to pick it up. Here's a roadmap to get started:
- Start with a good beginner's book or online tutorial.
- Familiarize yourself with the syntax and basic concepts.
- Practice by coding small programs and gradually increase complexity.
- Join coding communities and forums for support and guidance.
- Work on personal projects to apply what you've learned.
- Keep experimenting and stay up-to-date with the latest developments in C++.
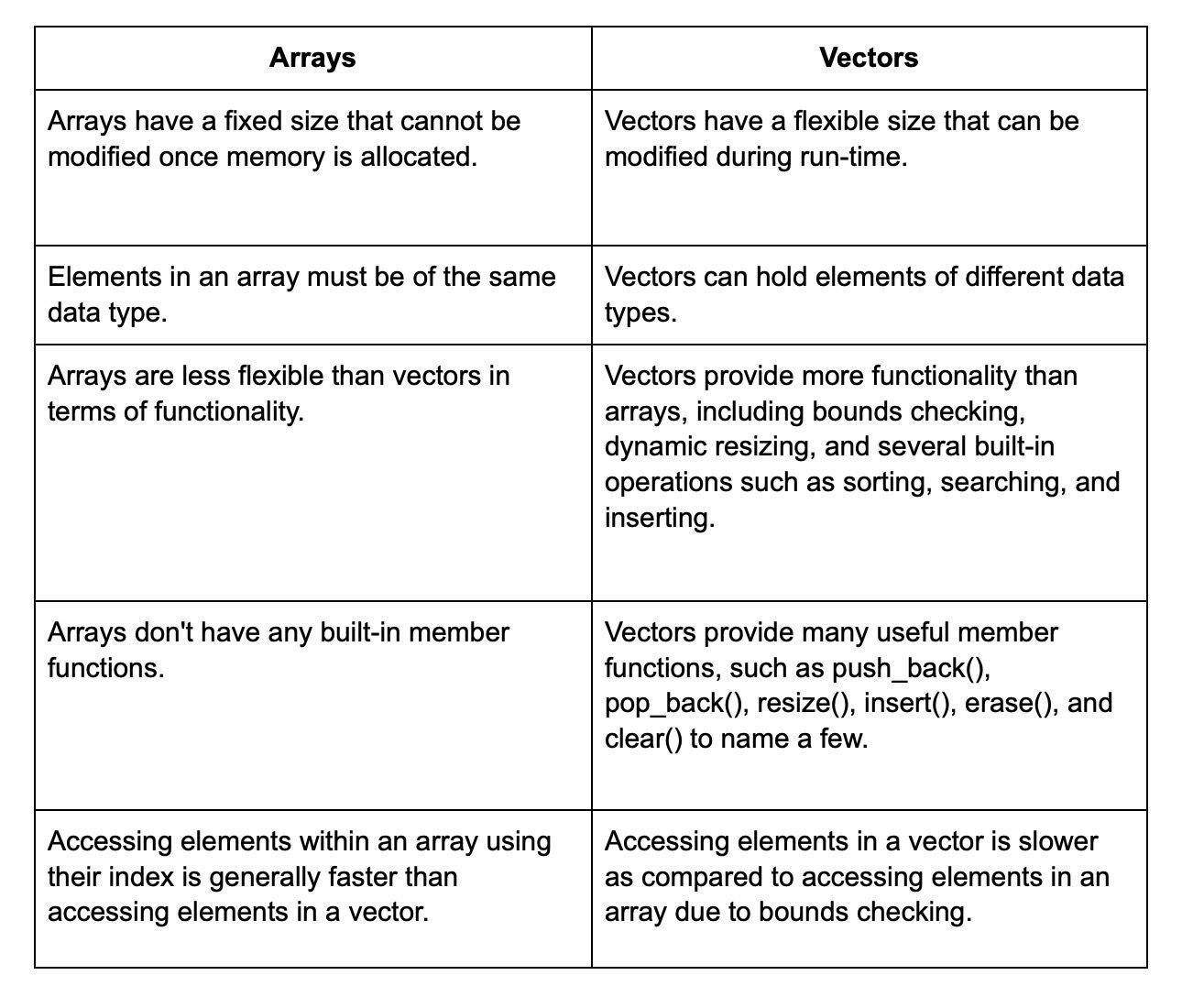
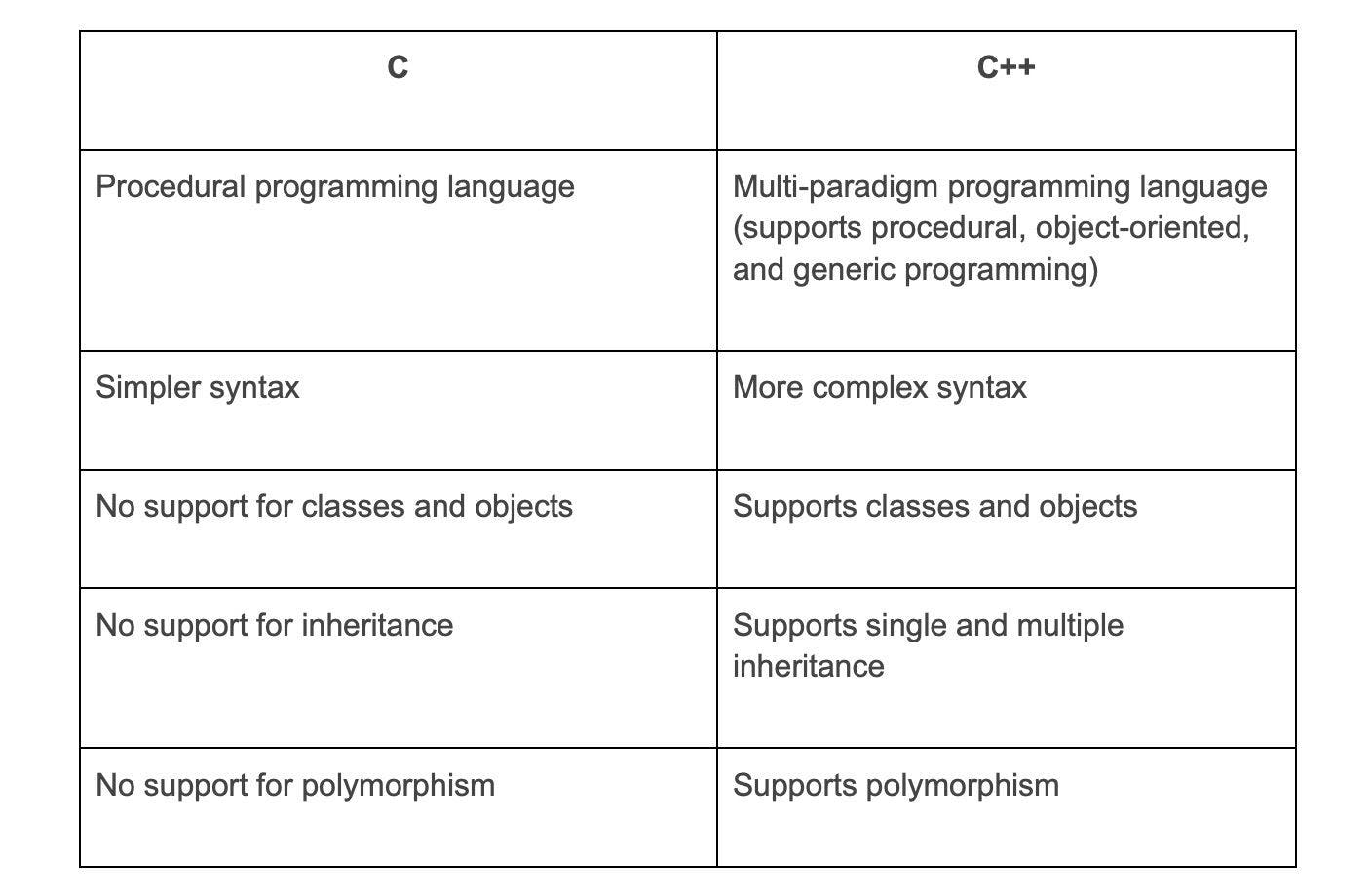
5. What is the difference between C and C++?
The differences between C and C++ are:
6. What is a template in C++?
In C++, a template is a feature that allows you to write generic programs that work with different data types. You can create a function or a class template which can then be used with different data types. The main advantage of using templates is that you can avoid writing the same code multiple times for different data types.
Templates also make code more reusable and easier to maintain. To create a function template, you use the keyword "template" followed by the template parameter list. You then define the function like you normally would. The template parameter list specifies the types that the template can work with.
Here's an example of a function template that finds the maximum of two values:

In this example, T is the template parameter that specifies the type of the arguments, x and y. This function can be used with any data type for which the comparison operator > is defined. For example, you can call this function with int arguments like this - max(3, 5) - and it will return 5.
7. What is using namespace std in C++?
Using namespace std is a C++ directive that allows you to access the elements of the std namespace without explicitly specifying it. This means you can directly use cout, endl, and other standard library elements without having to write std::cout, std::endl, etc.
However, using this directive may cause naming conflicts, especially if you have multiple namespaces. It's recommended to avoid using it in larger projects.
8. What is the return type of a function in C++?
In C++, a function can return a value of any valid data type, including built-in data types such as int, float, and double, as well as user-defined data types such as classes or structs. The return type of a function is specified in the function declaration by placing the return data type before the name of the function . For example, a function that returns an integer might have the following declaration:
int square(int x);
which specifies that the function takes an integer argument and returns an integer value.
9. How are function arguments passed in C++?
When a function is called with arguments passed by value, copies of the values of the arguments are made and passed to the function. Any changes made to the arguments within the function do not affect the original values in the calling code.
On the other hand, when a function is called with arguments passed by reference, the memory address of the arguments is passed to the function. This allows the function to directly access and modify the original values of the arguments in the calling code.
It is important to note that passing arguments by reference can have performance advantages over passing by value, especially when working with large objects or data structures. However, passing by value can be useful when you want to ensure that the original values are not modified by the function.
10. What is a function in C++?
In C++, a function is a self-contained block of code that performs a specific task. It can be thought of as a subprogram within a program. Functions are used to organize code, improve code reusability, and modularize the program.
A function has a return type, a name, and zero or more parameters. The return type specifies the data type of the value that the function will return (if any). The name is used to identify and call the function. The parameters are variables that hold values passed into the function.

11. What is a destructor in C++?
Keep a note of this C++ interview question to ask candidates or answer recruiters.
A destructor in C++ is a member function of a class that is responsible for cleaning up the resources used by an object of that class when it is destroyed. A destructor is invoked automatically when an object goes out of scope or is explicitly deleted.
It has the same name as the class with a tilde symbol(~) in front of it, and it does not take any arguments. The purpose of the destructor is to free up any memory or resources allocated to the object during its lifetime.
Here's an example of a destructor in a C++ class:

In this example, the constructor is responsible for initializing the object's data members, while the destructor is responsible for releasing any memory or resources allocated during the object's lifetime.
12. What is function overloading in C++?
Function overloading in C++ is a feature that allows a programmer to define multiple functions with the same name but different parameter lists. This means that you can define functions with the same name but different input/output behaviors, making your code more flexible and easier to read.
Function overloading offers a way to handle different types of data and perform different operations using a single function name.
13. What is STL in C++?
STL stands for Standard Template Library and it's a powerful library in C++ for working with sequences of data.
Here is an example of how to use it:

14. How to run a C++ program in cmd?
To run a C++ program in the command prompt, follow these steps:
- Open the command prompt by pressing Win + R and then typing cmd.
- Navigate to the directory where your C++ program is located using the cd command. For example, if your program is in the directory C:\Programs, you would use the command cd C:\Programs.
- Compile your C++ program using the appropriate compiler command. For example, if you have g++ installed, you can use the command g++ program.CPP-o program to compile the program and generate an executable file.
- Once the compilation is successful, you can run the program by typing its name and pressing Enter. For example, if your executable file is named program.exe, you would type program and press Enter.
- That's it! Your C++ program should now run in the command prompt.
Please note that the steps may vary slightly depending on the compiler and operating system you are using. The above steps assume th use of a compiler like g++ on a Windows operating system.
15. What is type casting in C++?
Type casting in C++ is a way to convert one data type into another. It helps in ensuring compatibility and flexibility in programming. C++ provides two types of casting: implicit and explicit.
Implicit casting is done automatically by the compiler, while explicit casting requires the programmer to explicitly convert the data type. This can be useful when working with mixed data types or performing specific operations.
16. How to use a string in C++?
To use a string in C++, you need to follow these steps:
Include the < string > header in your program by using the #include preprocessor directive:

Alternatively, you can initialize the string at the time of declaration:

Access and modify the string using various string member functions such as length(), substr(), append(), etc.
For example, to retrieve the length of the string, use the length() function:

If you want to extract a substring from the original string, you can use the substr() function:

Use the string in your program as needed. Also, it is important to include the necessary headers, declare the variable, and utilize the appropriate member functions to work with the string effectively.
17. What is stream in C++?
A stream in C++ is an abstraction that allows input and output operations. It represents a sequence of characters that are read from or written to a specific device such as the console or a file.
Streams provide a convenient way to handle input and output in a standardized manner. There are different types of streams such as the standard input stream (cin) and the standard output stream (cout).
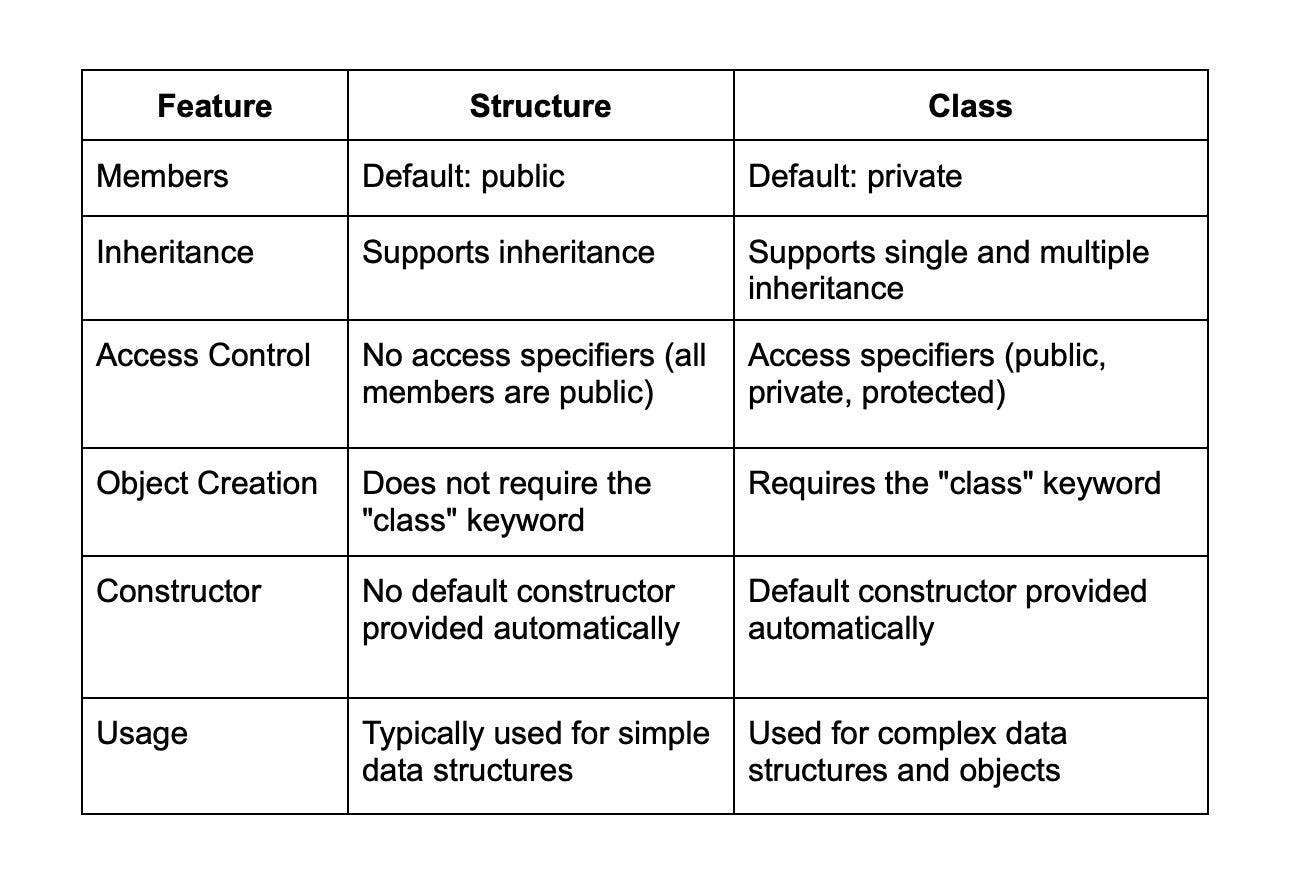
18. What is the difference between structure and class in C++?
19. How to clear the screen in C++?
A system-specific command can be used to clear the screen in C++. Here's an example using the standard library function system:

In the code above, std::system("clear"); clears the screen in Linux and macOS, while std::system("cls"); is used for Windows systems.
20. How to compile and run a C program in notepad++?
To compile and run a C program in Notepad++, you will need to set up a build system and configure the necessary commands. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Install a C compiler: You'll need a C compiler installed on your system to compile and run C programs. A popular option is MinGW for Windows, which provides the GCC compiler.
- Set up the compiler path: Once you have a C compiler installed, add the compiler's bin directory to your system's PATH environment variable. This allows Notepad++ to find the compiler when executing build commands.
- Configure Notepad++: Open Notepad++ and go to "Settings" -> "Preferences".
- Select the "Language" tab on the left sidebar and choose "C" from the "Language" dropdown.
- In the "Syntax Highlighting" section, select "C" as the default language for *.c files.
- Select the "Run" tab on the left sidebar and set up the following commands:
- Execute: Enter the command to run the compiled program. For example, if your compiled program is named "program.exe", you can use cmd /c "$(FULL_CURRENT_PATH)" as the command.
- Compile: Enter the command to compile the C program. For MinGW, you can use gcc "$(FULL_CURRENT_PATH)" -o "$(CURRENT_DIRECTORY)$(NAME_PART).exe" as the command. This command uses the gcc compiler to compile the current file and outputs the executable in the same directory with the same name as the source file.
- Click "OK" to save the settings.
- Open a new or existing C file in Notepad++.
- Press F5 or go to "Run" -> "Run" to compile and run the C program. This will execute the build commands configured in the previous steps.
- Make sure to save your C file with a .c extension before running the build commands.
Note: The instructions provided here are specific to using MinGW on Windows. If you are using a different compiler or operating system, you may need to adjust the commands accordingly.
21. How many keywords are there in C++?
There are a total of 95 reserved keywords in C++. These keywords have special meanings and cannot be used for re-definition or overloading.
Some examples of these keywords include "alignas", "auto", "bool", "class", "double", "for", "if", "namespace", "return", and "while".
22. What is iostream in C++?
In C++, iostream is a header file that is part of the standard library. It defines the standard input/output stream objects, such as cout (for output) and cin (for input). By including the iostream header, you can utilize these stream objects for reading from and writing to the standard input and output streams.

Using the iostream header is essential when working with input and output operations in a C++ program. Without including it, you won't be able to use the cout and cin stream objects.
23. How to give space in C++?
To give space in C++, use the "setw" function from the "iomanip" library. First, include the library by adding #include < iomanip> at the top. Then, use setw followed by the desired width to create an empty space.
For example, cout << setw(10); will create a space of 10 characters. Remember to use cout to display the space.
24. Which operator cannot be overloaded in C++ ?
The "scope resolution" operator (::) cannot be overloaded in C++. This operator is used to access global variables, functions, and classes from outside their defined scope. Not allowing overload ensures consistent behavior while accessing elements at various scopes.
Overloading other operators, however, gives flexibility and enables customized behavior for user-defined types.
25. What is a default argument in a function? How is it useful?
A default argument in a function in C++ is a parameter that has a predefined value assigned to it. It allows you to provide a default value for a function parameter, so if the caller does not provide a value for that parameter when calling the function, the default value will be used.
The syntax for declaring a default argument is to assign a value to the parameter in the function declaration. For example:

In the above example, the default value for the x parameter is 5. If the caller of the function does not provide a value for x, the function will use the default value of 5.
Default arguments are useful in several scenarios:
Convenience: Default arguments allow you to provide a default behavior for a function without requiring the caller to explicitly provide values for all parameters. This can make the function easier to use and reduce the amount of code needed to call the function.
Code reuse: By providing default arguments, you can define a single function that can be used in multiple scenarios with different parameter values. This promotes code reuse and reduces the need for duplicate code.
Gradual implementation: Default arguments are particularly useful when you want to add new parameters to a function without breaking existing code that calls the function. By providing default values for the new parameters, existing code can continue to work without modification, while new code can take advantage of the additional functionality.
26. What is an exception in C++?
An exception is an object that is thrown at runtime when an abnormal behavior or situation is encountered in a C++ program. It provides a way to transfer control and information from one part of the program to another part in order to handle the exceptional circumstance or error.
Exception handling in C++ involves throwing an exception using the throw keyword, catching it using the try-catch block, and handling it appropriately in the catch block.
27. What is the difference between C++ and Java?
C++ and Java differ in several ways:
Memory Management:
- C++ allows for manual memory management using features like pointers and new/delete. This gives the programmer more control but can also lead to memory-related errors if not handled carefully.
- Java uses automatic memory management through garbage collection. Developers do not need to explicitly deallocate memory, reducing the risk of memory leaks and pointer-related errors.
Language Paradigm:
- C++ is a multi-paradigm language that supports both procedural and object-oriented programming. It also includes features like templates for generic programming.
- Java is primarily an object-oriented language, and it encourages the use of classes and objects for structuring code.
Platform Independence:
- Java is known for its "write once, run anywhere" capability, as Java code is compiled into bytecode that can be executed on any platform with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
- C++ code is compiled into platform-specific machine code, which means that different binaries need to be generated for different platforms.
Exception Handling:
- C++ uses a combination of the try, catch, and throw keywords for exception handling.
- Java has a more robust and unified approach to exception handling using the try, catch, finally, and throw keywords.
Standard Library:
- C++ has the C++ Standard Library (STL) that provides a rich set of data structures (e.g., vectors, maps) and algorithms (e.g., sorting, searching) as part of the language.
- Java has its own standard library that includes data structures (e.g., ArrayList, HashMap) and utility classes (e.g., Collections, String) for common tasks.
Performance:
- C++ is often considered faster and more efficient than Java because of its lower-level memory control and direct compilation to machine code.
- Java provides platform independence and strong safety checks, but it may have a performance overhead due to interpretation or JIT compilation.
Ecosystem:
- C++ is widely used in system programming, game development, embedded systems, and areas where low-level control is essential.
- Java is commonly used in enterprise applications, Android app development, web services, and scenarios where platform independence is crucial.
28. What is stack in C++?
In C++, a stack is a container adapter in the C++ Standard Template Library (STL) that provides functionality of a stack data structure. It operates on a last-in, first-out (LIFO) basis, meaning that the last element to be added is the first to be removed. A stack can be implemented using other containers in C++ like vectors, lists, or deques.
29. What is conio.h in C++?
conio.h is a C++ header file that provides a collection of functions to read input and output to the console. It mainly includes functions, such as getch() and clrscr(), which are used to get a single character input from the user and clear the console screen respectively.
However, conio.h is a non-standard library and is not recommended to be used in modern programming practices.
30. What is a function prototype in C++?
A function prototype in C++ is a declaration of a function that specifies the function name, return type, and parameter types. It provides information to the compiler about the function's interface before the function is actually defined. A function prototype is typically placed in a header file, and is used to allow functions to be called before they are defined, as well as to ensure that functions are called with the correct types and number of parameters. The function definition provides the actual implementation of the function.
31. What is an iterator in C++?
An iterator in C++ is an object that points to elements in a sequence (like an array or a container). It allows you to traverse through the elements of the sequence and perform operations on them. It provides a way to access, modify, and delete elements in a sequential manner. An iterator is commonly used in loops and algorithms to process container elements one by one.
32. What is :: in C++?
In C++, "::" is the scope resolution operator. It is used to access entities (such as variables, functions, or classes) that are defined within a specific scope. By using "::", you can specify the scope in which the entity is defined, allowing you to avoid naming conflicts and access the correct entity. This operator is especially useful when working with namespaces and nested classes.
33. What is enum in C++?
An enum in C++ is a user-defined type that consists of a set of named constants. It allows you to define a set of named values which can be used as symbolic names for variables. The enum constants can be used to represent a finite set of values. This helps in writing clear and readable code by associating names to numerical values.
34. What is endl in C++?
endl is a special command in C++ that is used to insert a newline character and flush the output buffer. It is often used with the cout object to output text to the console. Using endl is equivalent to using "\n" to insert a newline character; however, endl also flushes the output buffer, ensuring that the text is immediately displayed.
35. How to save a file in C++?
The steps to save a file in C++ are:
- Include the < fstream > header.
- Create an ofstream object and open it using the open() method, specifying the desired file name.
- Use the << operator to write data to the file.
- Close the file using the close() method.
Remember to handle any errors that may occur during the file operations.
36. Which operators can be overloaded in C++?
In C++, operators can be overloaded to give special meaning to an existing operator for user-defined classes. The following operators can be overloaded in C++:
Arithmetic operators:
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (-)
- Multiplication (*)
- Division (/)
- Modulus (%)
Assignment operators:
- Assignment (=)
- Addition and assignment (+=)
- Subtraction and assignment (-=)
- Multiplication and assignment (*=)
- Division and assignment (/=)
- Modulus and assignment (%=)
Comparison operators:
- Equality (==)
- Inequality (!=)
- Less than (<)
- Greater than (>)
- Less than or equal to (<=)
- Greater than or equal to (>=)
Increment and Decrement Operators:
- Prefix increment (++)
- Postfix increment (++)
- Prefix decrement (--)
- Postfix decrement (--)
Logical operators:
- Logical NOT (!)
- Logical AND (&&)
- Logical OR (||)
Bitwise operators:
- Bitwise AND (&)
- Bitwise OR (|)
- Bitwise XOR (^)
- Bitwise complement (~)
- Bitwise left shift (<<)
- Bitwise right shift (>>)
Subscript operator:
- Array subscript ([])
Function call operator:
- Function call (())
Member access operators:
- Member selection (.)
- Member pointer selection (->)
It's important to note that not all operators can be overloaded in C++. These include:
- Scope resolution operator ( :: )
- Conditional operator ( ?: )
- sizeof operator
- typeid operator
- . operator for member access
- .* operator for member pointer access
37. How to include all libraries in C++?
You can use the "#include" directive before your code to include all libraries in C++. This allows you to access libraries and their functions. However, including all libraries is not recommended as it increases code size and may cause conflicts.
It is better to include only the necessary libraries for your specific program. Remember to use the libraries' header files and link the necessary libraries during the compilation process.
38. Can a function return multiple values in C++?
Yes, in C++ a function can return multiple values by utilizing various techniques. One approach is to use references or pointers as function parameters, allowing the function to modify the corresponding variables in the calling code. Another option is to use a std::tuple or std::pair to bundle multiple values together and return them as a single object.

39. What is an expression in C++?
An expression in C++ is any valid unit of code that can be evaluated to a value. It can be a combination of variables, constants, literals, operators, and functions that produce a single value. Expressions can be used for variable assignments, conditional statements, loop statements, and many other programming constructs.
For example, a + b * c is an expression in C++ that multiplies the value of b with c, adds the result to the value of a, and returns the final outcome as a single value.
40. Why is the namespace std used in C++?
Namespace std is used in C++ as an identifier to enclose the Standard Library. It is a collection of pre-written code that can be used with C++ to simplify common programming tasks.
Using namespace std provides access to the Standard Library entities, such as different types, functions, and variables, so that they can be used within a program without having to define them again. Therefore, when namespace std is used, it is no longer necessary to write code for every action to be performed. This makes coding more efficient.
41. Which is the best C++ compiler?
Choosing the best C++ compiler depends on your specific requirements and preferences. The choice of the best compiler depends on your specific project requirements, platform, and personal preferences. It's also worth considering factors like performance, standard compliance, and the availability of development tools and libraries. Many C++ developers work with multiple compilers depending on the target platform and project needs. Here are some widely used and respected C++ compilers, each with its own strengths that are widely used and recommended by C++ developers:
Visual C++ Compiler (Microsoft Visual Studio):
- Great for Windows development.
- Integrated development environment (IDE) with a rich set of tools.
- Excellent support for Windows-specific development.
Clang:
- Known for its high-quality diagnostics and error messages.
- Excellent C++ standards compliance.
- Often used in combination with CMake for cross-platform development.
GCC (GNU Compiler Collection):
- Highly portable and available on various platforms.
- Strong optimization capabilities.
- Good compliance with C++ standards.
Intel C++ Compiler:
- Known for excellent optimization, especially on Intel processors.
- Often used in scientific and high-performance computing.
MinGW-w64:
- Provides a Windows development environment with GCC.
- Suitable for cross-platform development targeting Windows.
LLVM (Low-Level Virtual Machine):
- Offers both Clang and other compiler frontends.
- Known for its modular and extensible architecture.
42. What are the different data types present in C++?
The following are the data types in C++:
- Primitive data types are built-in or predefined data types and can be used directly by the user to declare variables. Examples include integers, characters, floating-point numbers, booleans, and others.
- Derived data types are user-defined data types created by combining one or more primitive data types. Examples include arrays, pointers, and functions.
- User-defined data types are those defined by the user using classes or structures.
It's worth noting that each data type has its own size, range of values, and behavior.
43. What are the advantages of C++?
The advantages of C++ are:
Object-oriented language: C++ is an object-oriented programming language that allows developers to create flexible and reusable code. This makes it easier to maintain applications over time.
Efficient memory usage: C++ provides full control over memory management. It allows developers to implement dynamic memory allocation or deallocation and manage memory usage efficiently. It offers a more sustainable way of using memory than many other programming languages.
High portability: C++ is a highly portable language and is often the language of choice for multi-device, multi-platform app development. This ensures that developers can write and execute their code on different devices and operating systems.
Efficient compilation: C++ provides efficient compilation, which means that code compilation can be done in highly optimized computers with little or no overhead. This results in faster code compilation times and allows the code to execute faster.
Large community: C++ has a large community of developers who are continuously creating and contributing to the program. This ensures that C++ continuously evolves and improves.
Overall, C++ is an excellent programming language for developers who need high performance, flexibility, and control over memory management.
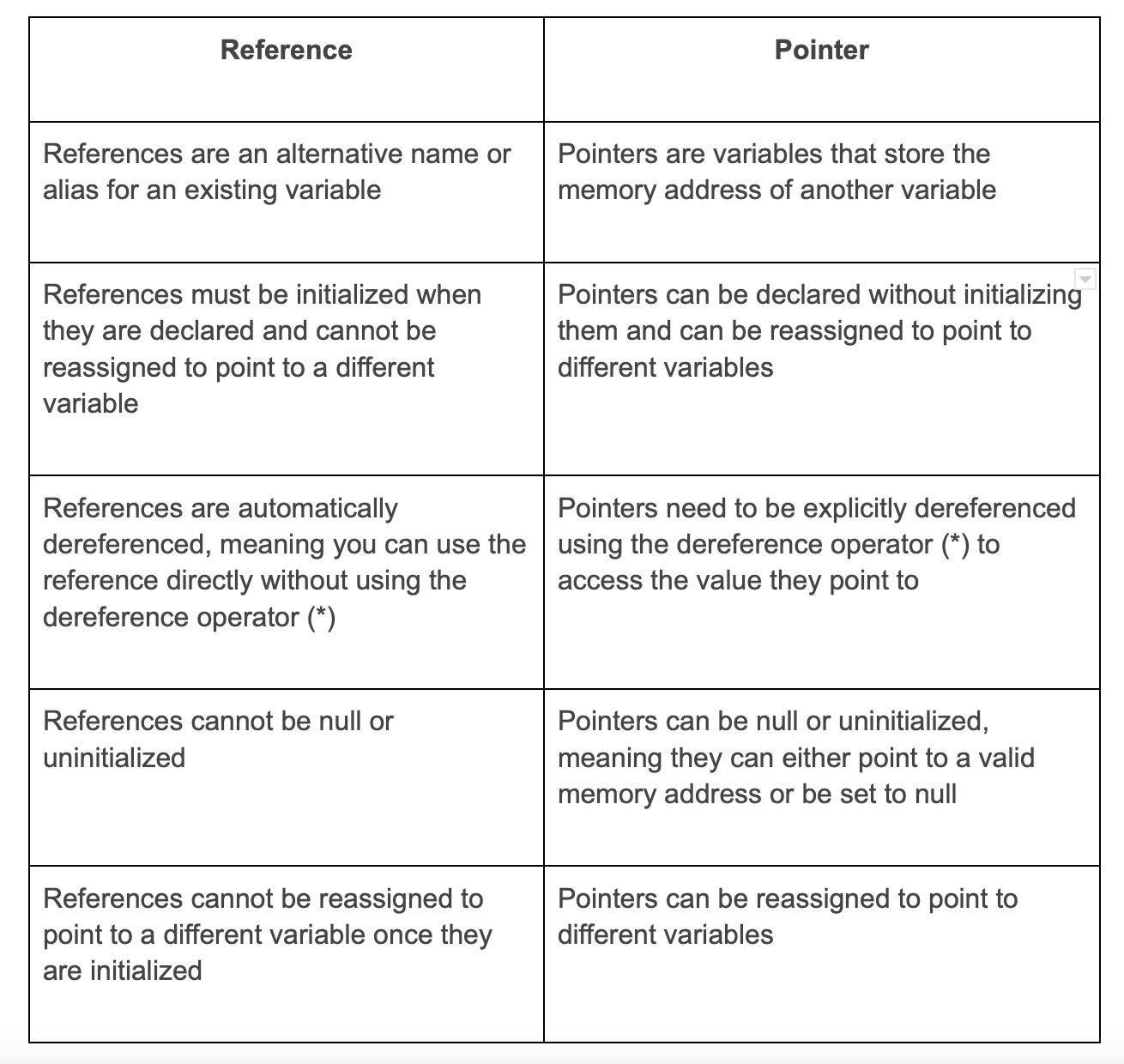
44. What is the difference between reference and pointer?
Reference and pointer have the following differences:
45. What is exception handling in C++?
Exception handling in C++ is a mechanism to handle errors or exceptional events that may occur during program execution. It allows you to catch and handle these exceptions instead of terminating the program abruptly. Using try-catch blocks, you can write code to handle specific exceptions and provide alternative solutions. This prevents crashes and helps make the code more robust and reliable.
46. What is Visual C++?
Visual C++ is a programming language that is part of Microsoft's Visual Studio IDE. It is primarily used for developing Windows applications. It has a range of features and libraries that make it easier to create graphical user interfaces and perform system-level programming.
Visual C++ supports both managed and unmanaged code and is commonly used for developing high-performance applications.
47. What is flush in C++?
In C++, "flush" is a function that ensures all data in the output buffer is printed immediately. It can be used to enforce printing before a program exits or to clear the output buffer. When using "cout", the "flush" function is often employed with the "endl" manipulator.
Flushing is especially important when dealing with output involving user input or file handling.
48. How does the compiler deal with vTable and vptr in C++?
vTable is a table that contains the function pointers. Additionally, vptr is a singular pointer to a vTable. Every class has a vTable; therefore, every object contains a vptr. The C++ compiler, to maintain and use vptr and vTable, adds some additional code to two places:
Constructor
vptr is set up by this code in every constructor: Of the object that is being made to point to the class's vTable
Polymorphic Function Call
The compiler adds code to look for vptr using the base class pointer or reference at every site where a polymorphic call is performed. Once the vptr has been properly obtained, the vTable of a derived class may be accessed. The vTable is used to obtain and call the address of the derived class method display().
This C++ interview question can show the interviewer the depth of your knowledge in the language.
Wrapping up
With the help of the C++ interview questions above, you’re all set to give a C++ interview. Alongside these, make it a point to practice your soft skills and show potential employers that you can work well with others. Likewise, recruiters can also use the questions above to take an interview to hire the ideal C++ developer.
If you’re a C++ programmer ready to take the next step in your career, apply at Turing. And if you’re a recruiter looking for exceptional C++ programmers to add to your team, visit Turing.com.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber C++ developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.