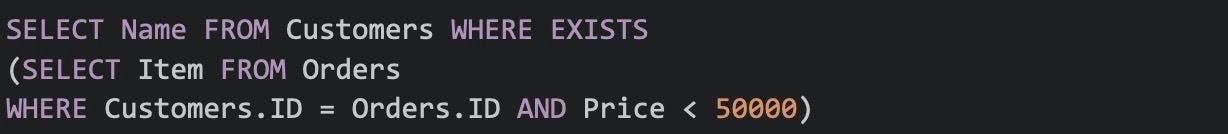SQL
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is Index in SQL?
With the help of Indexes, information retrieval from the database happens faster and with greater efficiency. Thus, indexes improve performance. There are three types of indexes:
- Clustered: Used for reordering tables and searching information with key values.
- Non-clustered: Used for maintaining the order of the tables.
- Unique: They ban fields from having duplicate values.
There can be many non-clustered indexes in a table, however, there can be only one clustered index.
2. What is a Synonym in SQL?
As the name suggests, a synonym is used to give different names to the same object in the database. In the case of object-renaming or object schema-change, existing applications can continue to use older names because of synonyms. A synonym must only reference an object and not another synonym. Additionally, synonyms can also be used to reference objects in different databases or servers, by using 3 or 4 part object names. There can be many names for a single database object as long as all the names directly refer to the same database object.
You must ensure that you know answers to such SQL interview questions as answering them correctly will give you the much-needed confidence for the more difficult ones.
3. Mention some advantages of Synonyms.
Below are some advantages of using Synonyms:
- Synonyms create a layer of abstraction for the specific object
- For objects, with complex 3 or 4 part names, residing on the same server, Synonyms can give a simpler alias
- Offers the flexibility to change object location without having to change the existing code
- When the name of an object is changed or dropped, Synonym offers backward compatibility for older applications
- Synonyms are also useful in front-end query tools such as Access linked tables and spreadsheets if there is a direct link to these tables
4. Are there any disadvantages to using Synonyms?
Yes, there are some disadvantages.
- Synonyms are only loosely linked to the referenced object and thus, can be deleted without warning when being used to reference a different database object
- Inside chaining cannot take place, meaning that the synonym of a synonym cannot be created
- One cannot create a table with the same Synonym name
- The checking for the object for which the Synonym is created happens at runtime and not at the time of creation. This means if there is an error, such as a spelling error, it will only show up at runtime creating a problem in accessing the object
- Synonyms cannot be referenced in DDL statements
For SQL interview questions that ask you to talk about the advantages or disadvantages of a certain component or tool, ensure that you list as many as you can. Also, you can make your answer to such an SQL interview question meaty by adding personal anecdotes about some of the advantages or disadvantages.
5. Are NULL values equal to zero?
No. NULL values show an absence of characters, whereas zero is a numerical value. NULL values occur when a character is unavailable or not known. NULL values should also not be confused with blank space because a blank space is not supposed to have any data attached to it, whereas a NULL value shows a data record without any value assigned to it.
6. What are Scalar subqueries and Correlated subqueries?
A Scalar subquery is when a query returns just one row and one column of data. A Correlated subquery occurs when a query cannot process without information from an outer query. In such cases, table aliases define the scope of the argument and the subquery is parameterized by an outer query. Thus, there is a correlation between the inner and outer queries. As a result, back and forth execution takes place where a single row of results from the outer query passes parameters to the inner query.
SQL interview questions like the one above try to ascertain the depth of your knowledge of SQL.
7. What is the difference between NVL and NVL2 functions?
The function NVL (exp1, exp2) is a conversion function that changes exp1 into the target exp2 under the condition that exp1 is NULL. The data type of exp1 is the same as that of a return value. The function NVL2 (exp1, exp2, exp3), on the other hand, is a checking function, which determines whether exp1 is null or not. When exp1 is not null, exp2 is returned as the result. When exp1 is null, exp3 is returned as the result.
8. What do you mean by ‘auto increment’?
With the auto-increment command, one can generate unique numbers when new records are added to a table. This function is especially useful when one wants to automatically generate the primary key field values upon inserting new records. This command comes in handy on several platforms. The auto-increment command for the SQL servers is “identity”.
9. What is the main use of ‘recursive stored procedure’?
The main use of the recursive stored procedure is to make the code calls till the time certain boundary conditions are reached. This helps programmers enhance productivity by using the same code multiple times.
An SQL interview question like this one shows that even though some of the advanced concepts may be easy to understand, they may be difficult to recount when suddenly faced with the question. Thus, when you prepare for SQL interview questions, ensure to revise all types of concepts.
10. Describe ‘datawarehouse’ in SQL.
A ‘datawarehouse’ is a system used for analyzing and reporting data. It is very similar to a physical warehouse where inventory is stored and assessed before being sent to a customer. Here, data is stored, analyzed, and reported. A datawarehouse functions as a central repository of data integrated from different areas and sources and makes this data available for use.
11. What is DBMS?
DBMS is an abbreviation for Database Management System for creating and managing databases. There are two types of databases:
- Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) - Data is stored in tables.
- Non-Relational Database Management Systems - Mostly referred to as NoSQL, stores data in non-tabular format.
12. What is the difference between SQL and MySQL?
Structured Query Language is utilized for handling and modifying data in relational databases. With SQL, you can generate and alter databases, tables, and other related objects, alongside executing various data operations, including record insertion, updates, and deletions.
MySQL, on the other hand, is a specific relational database management system (RDBMS) that uses SQL as its primary language for managing data. MySQL is an open-source RDBMS that is widely used for web applications,
13. List the type of SQL statements or subsets.
Below are the popular subsets used in SQL:
- DDL (Data Definition Language) - It is used to define and structure tables. Users can CREATE, ALTER, and DELETE the database tables.
- DCL (Data Control Language) - Administrators use it to give users privileges to GRANT or REVOKE permissions to the database.
- DML (Data Manipulation Language) - It allows users to either UPDATE, INSERT, RETRIEVE, or DELETE information from the database.
14. Define what joins are in SQL.
Joins is a statement used to join two or more rows based on their relationship. There are four types of Join statements:
- Left Join
- Right Join
- Inner Join
- Full Join
15. What is a Primary Key?
A primary key is used to identify unique rows or tables in a database. Primary keys must always contain unique values. Null or duplicate values are not considered primary keys.
16. What is a Foreign Key?
A foreign key is used to link two or more tables together. Its values match with a primary key from a different table. Foreign keys are like references between tables.
17. What is a unique key?
A unique key ensures a table has a unique value not found or contained in other rows or columns. Unlike the primary key, the unique key may have multiple columns. You can create a unique key using the keyword "UNIQUE" when defining the table.
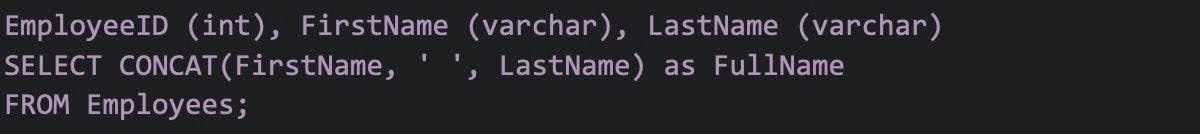
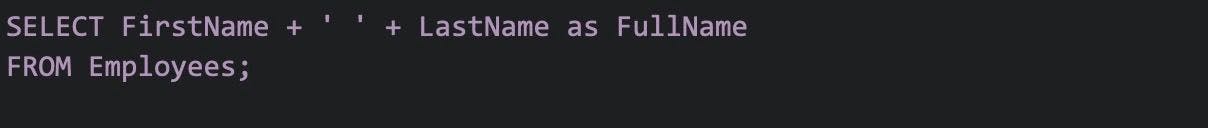
18. Create an employee table example.
Below is how to create an employee table:

19. What is a SELECT statement used for?
SELECT is a DML command used for fetching one or more tables. It queries for information which usually returns a set of results.
20. Name the clauses used in the SELECT statement.
WHERE - filters the rows according to their criteria
ORDER BY - Sorts the tables/rows according to the ASC clause (ascending order) or DESC clause (descending order)
GROUP BY - groups data from different tables that have similar rows in the database
21. What are CHAR and VARCHAR?
CHAR is a fixed-length string character, whereas VARCHAR is a variable-length string data structure. VARCHAR is preferred over CHAR because it is more space-efficient when storing strings with variable lengths.
22. List the types of relationships found in SQL.
One-to-one relationship - This relationship exists between two tables when a single row in one table corresponds to a single row in another table. This relationship is usually established using a foreign key constraint.
One-to-Many/Many-to-One - This relationship exists between two tables when a single row in one table corresponds to multiple rows in another table. This relationship is also established using a foreign key constraint.
Many-to-Many - This relationship exists between two tables when multiple rows in one table correspond to multiple rows in another table. This relationship is usually implemented using an intermediate table that contains foreign keys to the two tables being related.
23. What is the difference between TRUNCATE and DELETE?
The truncate command is used when you want to delete all rows and values from a table. It is a DDL type of command which is faster. While the DELETE command is used when you want to delete a specific row in a table. It is a DML command type and less efficient than the truncate statement.
24. What is a cursor?
A cursor is a temporary memory allocated by the server when performing any DML queries. They are used to store Database Tables. Basically a cursor in sql is an object in database code that allows processes to process rows one by one. While in other programming languages sets of data is processed individually through a loop, in SQL, data is processed in a set through a cursor.
Two types of cursors are Implicit cursors and Explicit cursors.
Implicit Cursors:
They are Default Cursors of SQL SERVER. Allocated when the user performs DML operations.
Explicit Cursors:
They are created by users in need. They are used for Fetching data from Tables in Row-By-Row Manner.
25. Define normalization.
Normalization is a method of breaking down larger, complex data into smaller tables. It helps in filtering unnecessary, redundant data and leaves only unique values.
26. What is ETL?
ETL is an acronym for Extract, Transform, and Load. It is a process where you extract data from different sources, transform the data quality, and finally load it into the database.
27. What is the difference between Local and Global variables?
Local variables are used inside a function and can’t be reused by other functions, whereas global variables can be accessed and used throughout the program.
28. What is a subquery?
A subquery is a query that is found in another query. Usually referred to as an inner query, its output is typically used by another query.
29. What is ACID?
ACID in SQL refers to a set of properties that guarantee the reliable and consistent processing of database transactions. It is an acronym where each letter stands for one of the properties:
Atomicity: Ensures that a transaction is either fully completed or not executed at all. If any part of a transaction fails, the entire transaction is rolled back, and the database remains unchanged.
Consistency: Guarantees that the database transitions from one consistent state to another upon the completion of a transaction. All data must adhere to predefined rules and constraints.
Isolation: Provides a degree of separation between concurrent transactions, ensuring that they do not interfere with one other. It helps maintain data integrity by controlling the visibility of changes made by one transaction to another.
Durability: Guarantees that after a transaction has been committed, the modifications made to the database become permanent, even if a system failure or crash occurs.
ACID properties are vital in maintaining data integrity and consistency in relational database management systems (RDBMS) and ensuring the robustness of transactions.
30. Define stored procedure.
A stored procedure is a function that contains a group of query statements that can be reused. They are stored inside a named object in the database and can be executed anytime they are required.
31. What are triggers in SQL?
Triggers are special stored procedures that run when there's an event in the database server, such as changing data in a table. A trigger is different from a regular stored procedure as it cannot be directly called like a regular stored procedure.
32. Define an ER.
An Entity Relationship (ER) diagram is a visual representation of the relationship tables found in the database. It displays the table structures and primary and foreign keys.
33. When are Triggers used?
Triggers in SQL are used to automatically enforce business rules or maintain data integrity by executing predefined actions in response to specific database events, such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. Common use cases include data validation, data auditing, and maintaining referential integrity or complex relationships between tables.
34. What are Sparse Columns?
Sparse columns are columns that provide optimized storage for null values. They reduce space that is usually taken up by null values and can be defined by using CREATE or ALTER statements.
35. Define Check Constraints.
Check constraints are used for checking and ensuring that values in a table follow domain integrity. Users can apply Check constraints to single and multiple columns.
36. What is Collation?
In SQL, collation refers to a set of rules that govern the proper ordering, comparison, and representation of characters in a particular character set or encoding. Collation influences how text data in a database is sorted, searched, and compared. It typically accounts for various linguistic considerations such as case sensitivity, accent sensitivity, and specific language-based conventions.
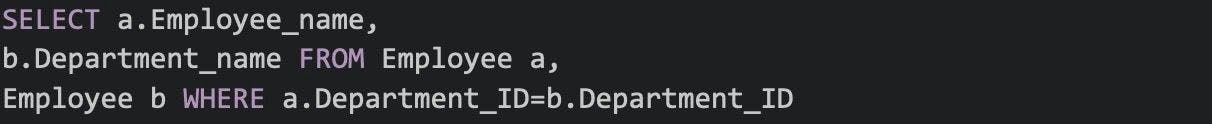
37. Write a SQL query for the salespeople and customers who live in the same city.
To write a SQL query that shows salespeople and customers who live in the same city, you need to have information about both salespeople and customers. Here's an example SQL query assuming you have two tables: salespeople and customers.
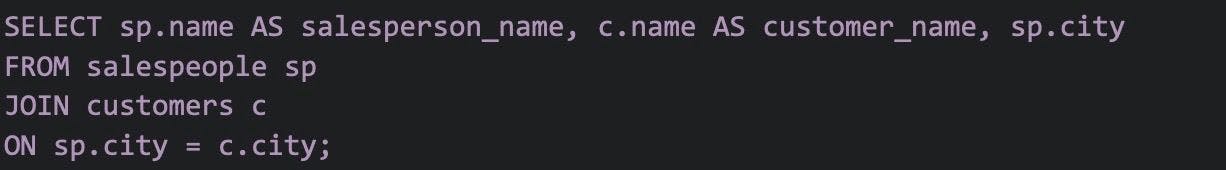
In this query, we're selecting the salesperson name, customer name, and city from two tables (salespeople and customers) using an INNER JOIN to connect them based on the condition that the city in the salespeople table equals the city in the customers table.
38. Write a SQL query to find orders where the order amount exists between 1000 and 5000.
To find orders with an order amount between 1000 and 5000, you can use the following SQL query:
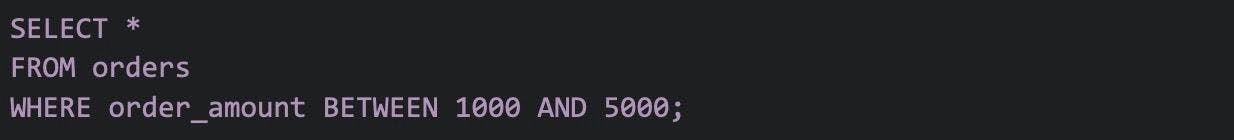
In this query, replace "orders" with the actual name of your orders table, and "order_amount" with the appropriate column name representing the order amount in your table. This query will return all rows where the order amount falls between 1000 and 5000, inclusive.
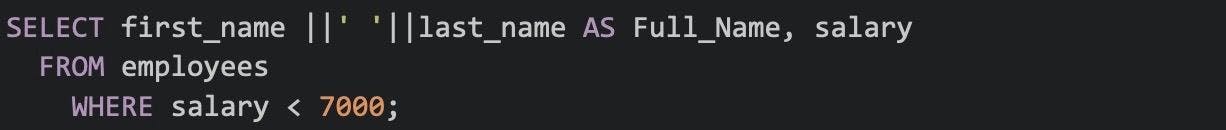
39. Write a SQL query to find those employees whose salaries are less than 7000.
40. What is a Filtered Index?
A filtered index is a non-clustered index that comes with optimized disk restore. It is created when a column has few values for queries. The purpose of a filtered index is to optimize query performance by reducing the size of the index and the number of index pages that need to be read. It helps in improving performance, storage reduction, and index maintenance.
41. What is a Clause?
A clause is one of the SQL query statements that filters or customizes data for a query. It allows users to limit the results by providing a conditional statement to the query. It is typically used when a large amount of data is in the database.
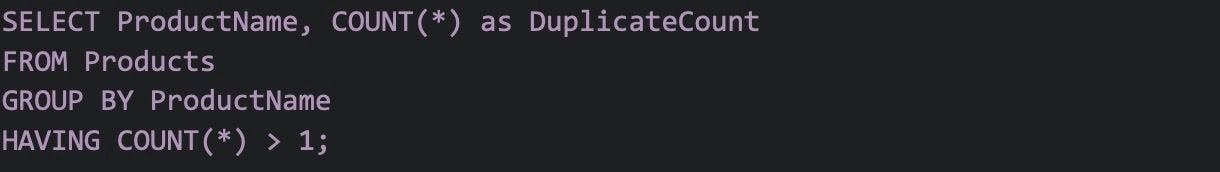
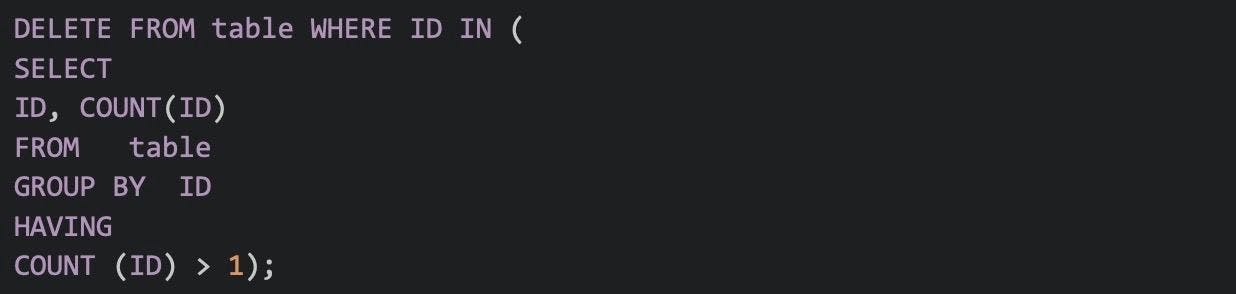
42. Write a SQL query that removes duplicates from the table.
The following SQL query removes the duplicate values
43. What is a Case Function?
A case function is a SQL logic that uses the if-then-else statements. It evaluates the conditions of a table and returns multiple result expressions.
44. Define a VIEW.
A view is a virtual table containing values in one or multiple tables. Views restrict data by selecting only required values to make queries easy.
45. What is a SCHEMA?
A schema in SQL is a collection of database objects, including tables, indexes, sequences, and other schema objects. It defines how data is organized in a relational database system. It is used to manage database objects and control access to them by different users.
46. Differentiate between HAVING and WHERE clauses.
These conditions are used for searching values except that the HAVING clause is used with the SELECT statement accompanied by the GROUP BY clause. The HAVING clause is used in combination with the GROUP BY clause to filter the data based on aggregate values, while the WHERE clause is used to filter the data based on individual values.
47. Define what is meant by CTE.
In SQL, a CTE (Common Table Expression) is a temporary result set, often used to simplify complex queries by breaking them into smaller, more manageable pieces. A CTE is created using the WITH clause and is available only within the context of the query that follows it.
48. What are SQL operators?
Operators are special characters or words that perform specific operations. They are used with the WHERE clause to filter data in most cases.
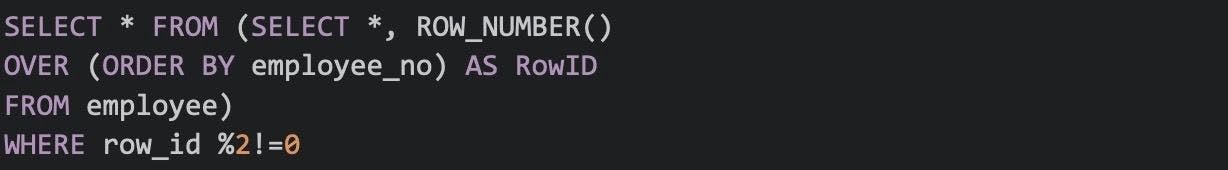
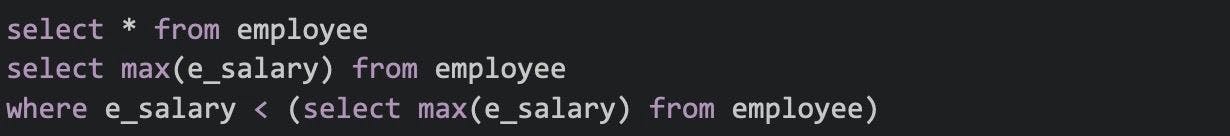
49. Write a SQL query to find the second-highest salary.
50. What is CDC?
CDC means change data capture. It records the recent activities made by the INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE statements made to the tables. It is basically a process of identifying and capturing changes made to data in the database and returning those changes in real time. This capture of changes from transactions in a source database and transferring them to the target, all in real-time, keeps the system in sync. This allows for reliable data copying and zero-downtime cloud migrations.
51. Define Auto Increment.
“AUTO INCREMENT” is a clause used to generate unique values whenever a new record is created and inserted into a table. It means that every time a new row is inserted into the table, the database system automatically generates a new value for that column.
52. What is a COALESCE?
COALESCE is a function that takes a set of inputs and returns the first non-null values. It is used to handle null values in a query's result set.
Wrapping up
Now that we have listed some of the most-asked SQL interview questions and answers that will help you better understand and prepare for technical interviews. It is important to practice writing complex queries and developing soft skills, as many companies seek problem-solvers and clear communicators.
With that in mind, if you are ready to tackle real-world challenges and earn better, apply to become one of the Turing SQL developers.
If you are a recruiter, you can also use these questions and answers to evaluate candidates' proficiency in SQL and ensure they have the necessary skills for the job. However, interviewing many candidates and finding the right fit for your company can take time and effort. Turing can help you hire the most talented SQL developers from around the world. Join Turing to build your dream development team.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber SQL developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.