MongoDB
Basic Interview Q&A
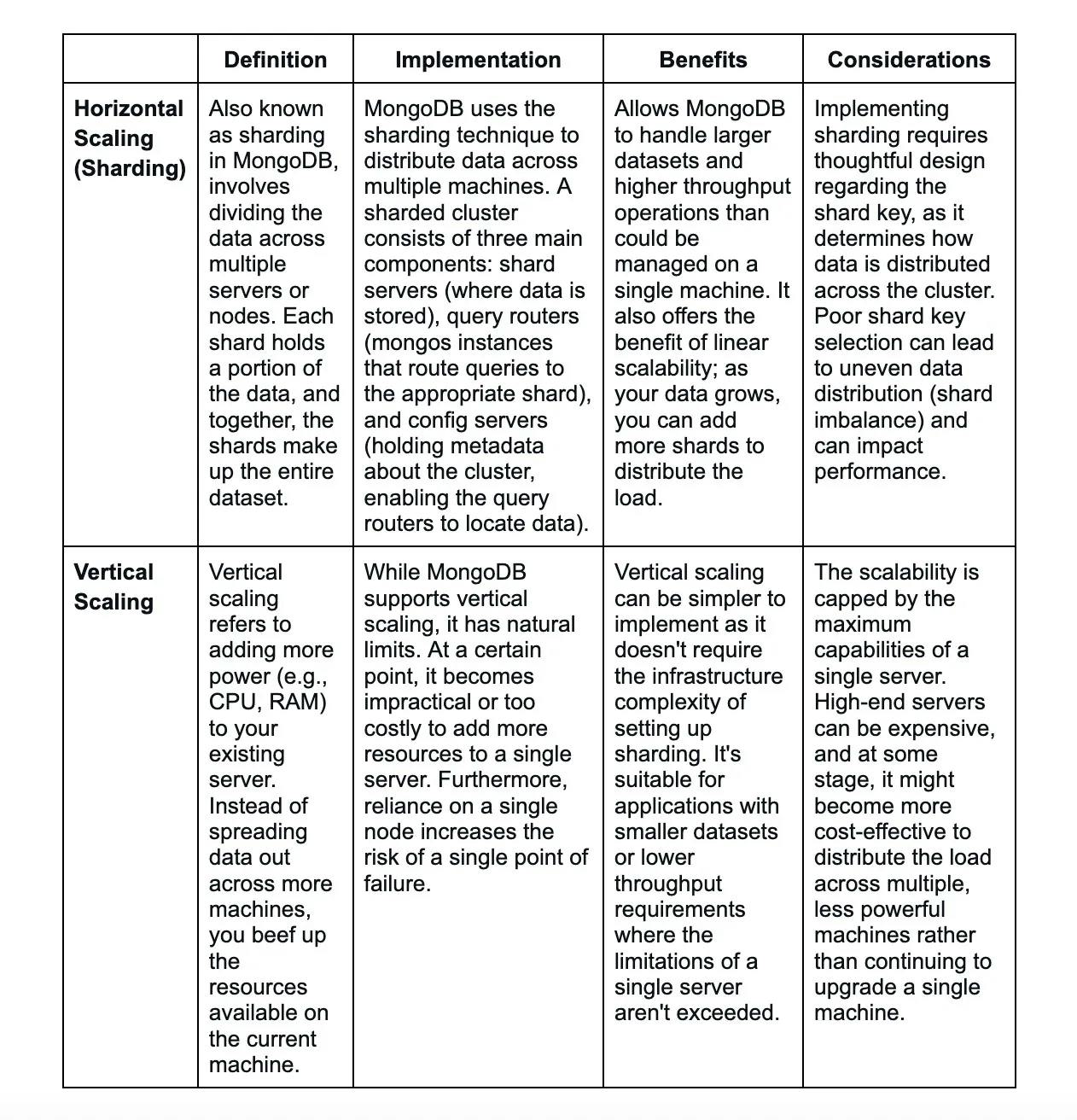
1. What exactly is sharding in MongoDB?
Sharding is the process of storing data records across many devices. It is a MongoDB strategy to meet data growth demands. It refers to the horizontal division of material in a database or search engine. Each partition is known as a shard or database shard.
2. What factors should be considered in MongoDB’s schema development process?
While developing a schema, one must consider the following:
Create your schema according to user needs.
If you use many objects together, combine them into a single document. Separate them if necessary.
In the schema, perform sophisticated aggregation.
3. What is the composition of Objecld?
Objectld is composed of the following:
Timestamp
Client machine ID
Client process ID
3 byte incremented counter
4. What are indexes in MongoDB?
Indexes are special structures in MongoDB that hold a subset of the data set in an easy-to-search format. The index maintains the value of a given field or collection of fields, ordered by the value of the field provided in the index.
5. What are the multiple languages supported by MongoDB?
MongoDB officially supports the following languages: C, C++, C#, Java, Node.js, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Scala, Go, and Erlang. We can use MongoDB with any of the languages mentioned above. There are several other community-supported drivers available, but MongoDB provides the ones described above.
6. What are the data models of MongoDB?
There are two types of data models in MongoDB. They are embedded and normalized data models. The structure of documents has an impact on data modeling. In MongoDB, related data can be incorporated into a single document structure (embedded data model). The relationship between data is stored through references from one document to another. It's known as the normalized data model.
7. What is a profiler's role in MongoDB?
MongoDB includes a database profiler that displays information about the performance of each database activity. You can use this profiler to discover queries (and write operations) that are taking longer than they should and use that information to determine when an index is required.
8. What is MongoDB and how does it differ from traditional relational databases?
MongoDB is a NoSQL, document-oriented database that stores data in a flexible, JSON-like format called BSON (binary JSON). Unlike traditional relational databases, it does not require a predefined schema, allowing for dynamic and hierarchical data storage. It is also designed to scale horizontally, making it suitable for handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data.
9. Explain BSON in MongoDB.
BSON, short for Binary JSON, is a binary-encoded serialization format that MongoDB utilizes to store documents in collections and facilitate data exchange. While it is similar to JSON in terms
One of the key extensions BSON offers over JSON is the support for additional data types. For instance, whereas JSON only supports text and numbers directly, BSON introduces types like Date, Binary data (such as images or encrypted content), and ObjectId (used for unique document identifiers), among others. These extended data types are critical for applications that require the storage of complex and varied data structures.
Furthermore, BSON's binary nature significantly enhances MongoDB's performance. The storage and retrieval of data are optimized, allowing for faster access to documents. This is particularly beneficial in environments where rapid processing of large volumes of data is essential.
10. What is a collection in MongoDB?
In MongoDB, a collection represents a grouping of MongoDB documents that are typically related to each other in some way. Analogous to a table in a traditional relational database management system, collections serve as the primary organizational structure for data in MongoDB. However, unlike tables in relational databases, collections in MongoDB offer a high degree of flexibility due to their lack of a fixed schema.
This schema-less nature means that within a single collection, documents can have different fields. For example, one document in a collection could contain ten fields, while another document in the same collection might contain only five fields or might contain a completely different set of fields. This flexibility allows developers to work with more varied data structures and to iterate more rapidly on their applications without needing to modify a rigid database schema each time the data structure changes.
11. Explain the structure of a MongoDB document.
A MongoDB document is structured as a BSON (Binary JSON) object, which is a binary representation of JSON-like documents. Like JSON, BSON supports the embedding of key-value pairs but with some extensions. Each key in a document is a field name, and the value associated with that key can be of various data types such as string, integer, boolean, array, another document (object), or even a BSON-specific type like ObjectId, Date, and Binary data.
One of the powerful features of MongoDB documents is the ability to nest documents within documents. This structure allows for a highly flexible and hierarchical organization of data, which can be particularly useful for representing complex relationships and data models.
12. What is a primary key in MongoDB?
In MongoDB, the primary key serves as a unique identifier for each document within a collection, ensuring the distinguishability of each document. Unlike some databases where you may need to explicitly define the primary key, MongoDB automatically generates an "_id" field for each document if it is not provided. This "_id" field is indexed, guaranteeing quick data retrieval using the primary key.
The default "_id" field uses ObjectId, a 12-byte BSON type, combining the timestamp, machine identifier, process ID, and a sequence number to ensure uniqueness across a distributed system. This design choice caters to scalability and fast generation of unique identifiers in distributed environments.
Although MongoDB automatically generates an "_id" field, developers have the flexibility to assign custom values to this field, provided they uphold the uniqueness constraint. This allows the integration of MongoDB into systems with existing identification schemes or the use of more domain-specific identifiers.
13. How do you find documents in MongoDB?
Finding documents in MongoDB is primarily achieved through the find() method, a versatile and powerful function that allows for both simple and complex queries against the documents in a collection.
For a simple use case, to retrieve all documents in a collection, you execute db.collectionName.find({}). This command queries without any filter, denoted by the empty braces {}, and returns all documents within collectionName.
14. What is an index in MongoDB and why is it important?
An index in MongoDB is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a collection. It works similarly to an index in a book, allowing MongoDB to quickly locate and access specific data without scanning the entire collection. Indexes are crucial for optimizing query performance.
15. What is the aggregation framework in MongoDB?
The aggregation framework in MongoDB is an advanced, functional feature designed to process data and aggregate information from documents within a collection. This feature leverages a staged, pipeline model which allows you to transform and combine data in multiple steps, each building upon the last, to achieve complex data processing and aggregation results.
16. What is the role of the _id field in a MongoDB document and can it be customized?
The "_id" field is the primary key in a MongoDB document that uniquely identifies each document within a collection. While MongoDB auto-generates "_id" values, you can also customize this field if you need specific values or want to use a different field as the primary key.
17. How do you delete documents in MongoDB?
You can delete documents in MongoDB using the deleteOne() or deleteMany() methods, depending on whether you want to delete a single document or multiple documents that match specific criteria.
18. Explain the difference between findOne() and find() in MongoDB.
In MongoDB, both findOne() and find() methods are used to retrieve documents from a collection, but they differ in their operation, return types, and intended use cases.
findOne():
- The findOne() method searches for the first document that matches the query criteria and returns it as a single document object. This method is particularly useful when you are looking for a specific document or know that your query criteria match a unique document in the collection.
- If findOne() does not find any matching document, it returns null, indicating that no document meets the search criteria.
- Given its nature of returning a single document, findOne() is suited for queries where you expect a single result, such as retrieving a user profile based on a unique username or ID.
find():
- Conversely, the find() method retrieves all documents that match the query criteria and returns a cursor to these documents. This cursor is an iterable object that lazily fetches the documents in batches as you iterate over it. This method is ideal for queries where multiple documents may meet the criteria, and you wish to process or display these documents.
- If find() finds no matching documents, it returns an empty cursor, effectively behaving as if querying an empty collection.
- Since find() returns a cursor, it is commonly used with cursor methods like .limit(), .sort(), and .toArray() to refine the results, manage large sets of results, and convert the results to an array, respectively.
19. What is a cursor in MongoDB and how is it used?
In MongoDB, a cursor is a powerful concept and tool that serves as an iterator to navigate through the results of a query. When a find() operation executes, instead of immediately returning all matched documents, MongoDB provides a cursor to these results. This cursor points to the query results in a manner that allows for efficient retrieval and manipulation of data, one document at a time or in batches.
Cursors are particularly useful for handling large datasets that might be too memory-intensive to load and process all at once. With cursors, MongoDB fetches documents in manageable batches, reducing the load on both the database and application memory.
20. How can you limit the number of documents returned in a MongoDB query?
In MongoDB, controlling the number of documents returned by a query is straightforward and efficient with the use of the limit() method. This method takes an integer value as an argument, which specifies the maximum number of documents that should be returned from a query. It’s particularly useful in scenarios where you need to paginate results or simply prevent overloading your application with too much data at once.
Syntax:
db.collection.find(query).limit(number)
Here,
- db.collection is the path to your collection.
- find(query) is your search criteria. If you want all documents, you can use an empty object {}.
- limit(number) specifies the maximum number of documents to return.
21. What is aggregation in MongoDB and why is it useful?
Aggregation in MongoDB is a robust process designed for data analysis and transformation within collections. It involves consolidating data from multiple documents to perform complex groupings, calculations, and generate aggregated results. This capability is essential for transforming document-shaped data structures into a summarized form, making it easier to understand trends, patterns, and anomalies in your data.
The aggregation framework in MongoDB operates through a pipeline mechanism, where data passes through multiple stages of transformation. Each stage in the pipeline processes the data as it flows through, performing operations such as filtering, grouping, sorting, and combining data, as well as other sophisticated calculations and data transformations. This pipeline architecture not only ensures flexibility in how operations are composed but also efficiency in processing large volumes of data.
Why Aggregation is Useful:
Data Summarization: Aggregation is invaluable for summarizing data, such as calculating sums, averages, and other statistical measures across large datasets. For instance, businesses might use aggregation to aggregate sales data to find total sales per region or to calculate average sales per product.
Transforming Data: It allows for the transformation of data into a structure that is more conducive to the specific requirements of an application or analysis. This could involve reshaping data, enriching documents with computed fields, or filtering out unnecessary data.
Complex Analytics: The aggregation framework enables complex analytical operations that can rival those of traditional relational databases. This includes the ability to join documents, perform cross-collection queries, and create complex hierarchical data structures.
Performance Optimization: By leveraging the aggregation pipeline, MongoDB can optimize query performance, especially when operating on indexes and when processing is distributed across multiple nodes in a cluster. This makes aggregation an efficient choice even for data-intensive operations.
22. How do you perform a case-insensitive search in MongoDB?
To perform a case-insensitive search, use regular expressions with the $regex operator and set the $options to "i", indicating case-insensitive matching. For example,
db.collectionName.find({ field: { $regex: "searchTerm", $options: "i" } }).
23. What is the $push operator in MongoDB and how does it work?
The $push operator in MongoDB is used to add elements to an array field within a document. It appends the specified value(s) to the array. For example:
db.collectionName.update({ _id: ObjectId("documentId") }, { $push: { fieldName: valueToPush } }).
24. Explain the concept of replication in MongoDB.
Replication in MongoDB is a method used to ensure the robustness and reliability of data by creating multiple copies of that data across different database servers or instances, collectively known as replicas. The primary mechanism through which MongoDB achieves replication is through a configuration called a replica set.
A replica set is a group of MongoDB servers that maintain the same data set, providing redundancy and high fault tolerance. Within a replica set, one server takes the role of the primary node, and the remaining servers are designated as secondary nodes. The primary node receives all write operations. Meanwhile, the secondary nodes replicate the data from the primary node and can serve read operations, thereby distributing the data access load and ensuring the system's scalability and performance.
25. What is a capped collection in MongoDB and when would you use it?
Capped Collections in MongoDB represent a special type of data storage with a fixed size. Once the allocated space is filled, the collection behaves like a circular buffer, automatically overwriting the oldest documents with new ones. This functionality is intrinsic to capped collections and does not require any additional data management logic in your application code.
Capped collections are particularly suited for scenarios where data volume management and retrieval speed are critical, but where historical data has diminishing value over time. Common applications include
- Logging: Ideal for log data where only recent entries are of interest. Capped collections can efficiently store logs by automatically purging the oldest entries, thus maintaining a manageable dataset size.
- Caching: Serve as a simple, performance-optimized caching mechanism where older entries naturally make way for newer ones once the collection reaches its size limit.
- Real-time Analytics and Monitoring: Useful for storing data points for recent activities, allowing for efficient queries on recent data for dashboarding or monitoring purposes.
26. Explain the concept of write concern in MongoDB.
Write Concern in MongoDB is a critical feature that enables clients to customize the level of assurance and acknowledgment they receive for write operations (inserts, updates, deletions) to the database. It’s a mechanism that allows the tuning of consistency and durability guarantees against the performance overhead inherent in distributed systems.
Write concern can be configured at different levels, including per-operation, per-connection, or as a default setting for the database. Here's an example of specifying a write concern for an insert operation:
db.collection.insert(
{ item: "product", qty: 100 },
{ writeConcern: { w: "majority", j: true, wtimeout: 5000 } }
)
27. How do you perform a regular expression-based search in MongoDB?
You can use the $regex operator in MongoDB to perform regular expression-based searches. For example:
db.collectionName.find({ field: { $regex: /pattern/ } }).
28. What is the $addToSet operator in MongoDB and how does it differ from $push?
The $addToSet operator is utilized to add a value to an array field within a document, but only if the value does not already exist in the array, thereby preventing duplicate entries. This behavior ensures that the array remains a set, where each element is unique. It is particularly useful when maintaining lists that require uniqueness, such as tags, categories, or permissions.
29. How can you drop a collection in MongoDB?
You can drop a collection in MongoDB using the drop() method. For example:
db.collectionName.drop().
30. What is the default port number for MongoDB and how can you change it?
The default port number for MongoDB is 27017. You can change it by specifying a different port number in the MongoDB configuration file or using the --port option when starting the MongoDB server.
31. Explain the difference between the update() and updateOne() methods in MongoDB.
In MongoDB, updating documents is a common operation, and understanding the distinction between the update() and updateOne() methods is crucial for optimizing database interactions and ensuring the intended outcomes of update operations.
update() Method:
- The update() method is designed to update multiple documents within a collection that match the given query criteria. By default, without specifying any additional options, update() will only modify the first document that matches the criteria.
- To update all documents that match the criteria, you must explicitly set the { multi: true } option in the update call. This is an essential distinction because failing to set this option when intending to update multiple documents can lead to unexpected results.
updateOne() Method:
- On the other hand, updateOne() targets a more specific use case. This method updates only the first document that matches the specified criteria and then stops, regardless of how many documents actually match.
- updateOne() is inherently designed to be precise, ensuring that only a single document is modified during an operation. There is no need to specify a { multi: true } option because the method's behavior is to update a single document by design.
32. What is the significance of the ObjectId data type in MongoDB?
ObjectId is a BSON data type used extensively in MongoDB as a primary key for documents, known as the _id field. It's designed to have a high probability of being unique across collections and even across different MongoDB clusters. Understanding its structure and significance is crucial for database modeling, data retrieval, and system design in MongoDB applications. An ObjectId is a 12-byte BSON type, ensuring a compact and efficient representation.
Significance of ObjectId data type:
- Uniqueness: The structure of ObjectIds ensures a high probability of uniqueness across documents, collections, and databases, mitigating the risk of collisions.
- Efficient Indexing: ObjectIds are automatically indexed, making retrieval operations using the _id field fast and efficient.
- Implicit Time Ordering: The timestamp component enables users to derive the creation time of a document directly from its _id, offering a helpful, built-in temporal sorting or filtering mechanism without additional fields or indexes.
- Scalability and Distributed Nature: Given its components (machine and process identifiers), the ObjectId generation process is well-suited for distributed environments, allowing various machines and processes to generate ids concurrently without central coordination
33. How do you create a backup of a MongoDB database?
You can create a backup of a MongoDB database using tools like mongodump or by taking file system-level backups. mongodump is a built-in MongoDB tool that creates a binary export of the database that can be restored using mongorestore.
File system-level backups involve copying the entire database directory while the database is in a consistent state.
Wrapping up
The top 100 MongoDB interview questions and answers provided in this blog offer a comprehensive overview for both interviewers looking to assess candidate proficiency and candidates aiming to solidify their MongoDB knowledge. These questions span basic concepts, intermediate topics, and advanced techniques, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of MongoDB's capabilities, best practices, and performance optimization strategies.
Turing plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between talented professionals and the companies that need them. By leveraging its advanced AI-based matching system, Turing carefully assesses the skills and expertise of developers, including their proficiency in MongoDB, to match them with positions that best fit their talents and career aspirations. This precision in matchmaking ensures that developers are not only challenged to grow but are also placed in roles where they can make the most significant impact.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber MongoDB developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.