PHP
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is the relationship between PHP and HTML?
PHP scripts can generate HTML, and information can be passed from HTML to PHP.
HTML is a client-side language, while PHP is a server-side language. So PHP runs on the server and returns texts, objects, and arrays, which we then utilize to display the values in HTML. This engagement aids in bridging gaps and the effective usage of both languages.
2. Talk about the significance of Parser in PHP?
A PHP parser is a piece of software that translates source code into computer-readable code. The parser converts whatever set of instructions we provide in the form of PHP code into a machine-readable format.
The token gets all() functions in PHP that can be used to parse PHP code.
3. What do you mean by hashing passwords?
Hashing a password is a method of transforming a single password into a hashed password string. The hashed password is usually one-way, meaning we can't move from the hashed password to the original password. So the question is why we needed to utilize hashing to perform all of this; why do extra work when we can just record our passwords as a simple string in the database? All of this is being done just to improve security so that hackers do not steal credentials from our valued site. md5, crypt, sha1, and bcrypt are some of the most often used cryptographic algorithms in PHP. The bcrypt hashing algorithm is the most widely used presently.
4. What are the main types of errors?
The primary types of errors are:
- Notices: Notices are non-critical errors that can occur while the script is being executed. Users won’t see these. Using an undefined variable as an example.
- Warnings: Warnings are more important than notices. The script execution is not interrupted by warnings. These are viewable by default. Include() a file that does not exist, for example.
- Syntax or Parsing error:- A forgotten quote mark, a missing semicolon at the end of a line, missing parenthesis, or excess characters are all examples of syntax errors. The PHP parser is unable to read and comprehend the code correctly, resulting in a parse error.
- Fatal: This is the most serious error of kind, and when it happens, the script's execution is immediately terminated. An example of a fatal error is accessing a non-existent object's property or calling need() on a non-existent file.
5. What are the processes for setting up a new database with MySQL and PHP?
The 4 primary steps used to create a new MySQL database in PHP are given below:
- The PHP script is used to establish a connection to the MySQL server.
- The connection has been verified. You can test the connection by writing an example query.
- The queries for the database are typed in and then saved in a string variable.
- Then, one by one, the constructed queries will be run.
6. In PHP, what is PDO?
PHP Data Object (PDO) is an acronym for PHP Data Object. PDO is a PHP extension that includes a core PDO class as well as database-specific drivers. Any database written for the PDO driver can be accessed using the PDO extension. PDO drivers are available for databases such as FreeTDS, Microsoft SQL Server, IBM DB2, Sybase, Oracle Call Interface, Firebird/Interbase 6, and PostgreSQL.
It provides a data-access abstraction layer that is lightweight and vendor-neutral. As a result, the function to issue queries and fetch data will be the same regardless of which database we utilize. It also concentrates on data access abstraction rather than database abstraction.
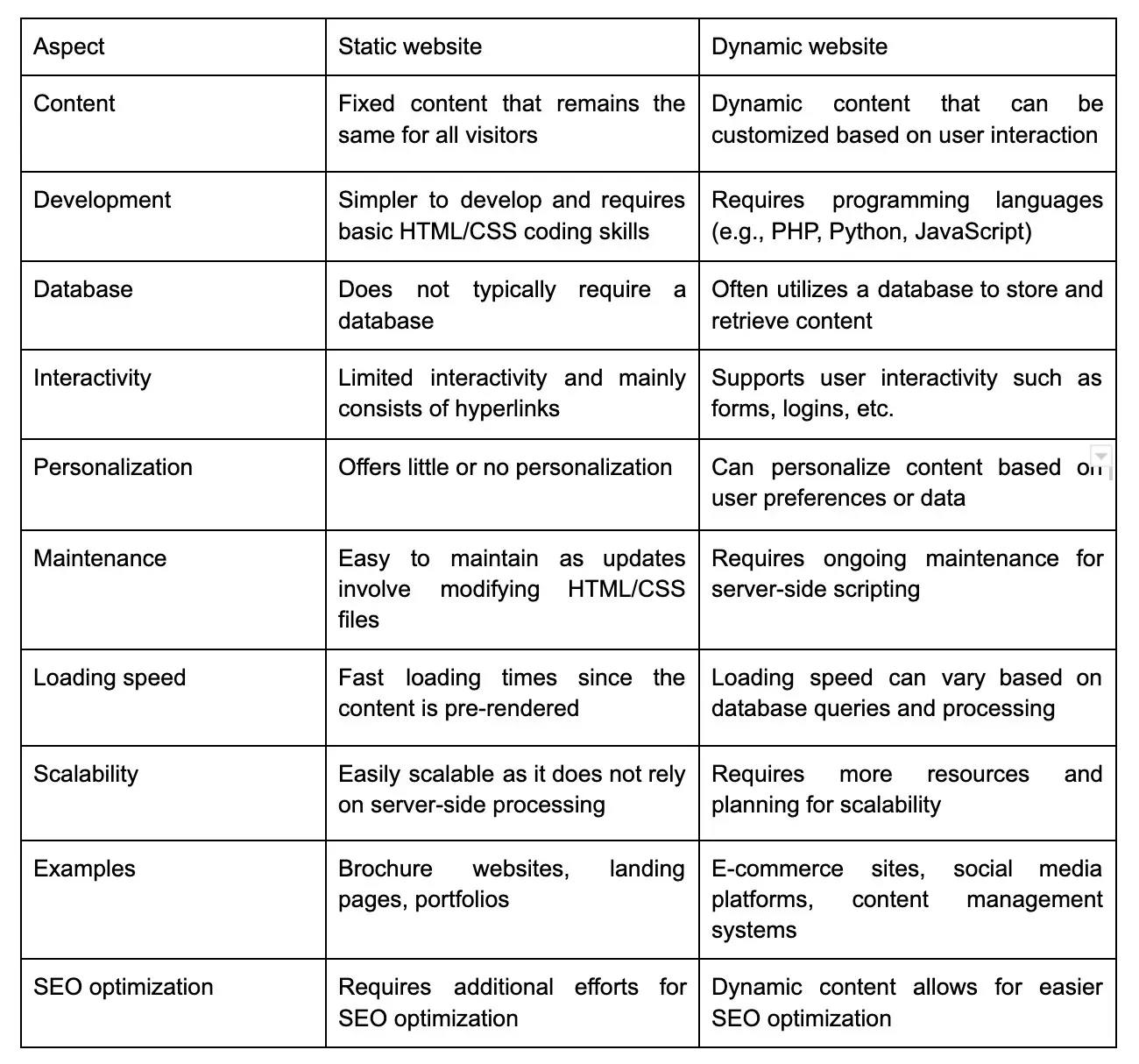
7. What is PHP and what are the advantages of using PHP?
PHP is a widely-used scripting language primarily designed for web development. It stands for "Hypertext Preprocessor" and is embedded within HTML code. PHP enables dynamic content creation, database connectivity, and server-side scripting. With its extensive community and rich set of features, it has become one of the most popular languages for building dynamic websites and web applications.
PHP offers several advantages for web development:
- It has a low learning curve, which makes it accessible to beginners.
- It's an open-source language with a large community, and has extensive documentation and support.
- It is platform-independent, which means it can run on various operating systems.
- It has robust database integration, offers great performance, and has a wide range of frameworks and libraries available for efficient development.
8. What are the rules for naming a PHP variable?
- Variable names must start with a dollar sign ($) followed by a letter or underscore.
- After the initial dollar sign, you can use any combination of letters, numbers, and underscores.
- Variable names are case-sensitive, so $myVariable and $myvariable are treated as different variables.
- You cannot use reserved words or PHP keywords such as if, else, foreach, etc., as variable names.
- Variable names should be descriptive and meaningful to improve code readability.
Here are some examples of valid variable names in PHP:

9. What is a PHP file?
A PHP file is a text file that contains PHP code, typically with a .PHP extension. It is an integral part of building dynamic web pages and applications. A PHP file can include a combination of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and PHP code. This versatility enables developers to integrate dynamic functionalities with the presentation layer.
When a client's web browser requests a PHP file, the server processes the PHP code within the file before sending the final output to the browser. This server-side execution allows developers to create dynamic and interactive content for the users.
10. What is a PHP function?
A PHP function is a named block of code that performs a specific task and can be reused throughout a program. It encapsulates a set of instructions, accepts input parameters (optional), and can return a value (optional).
Functions help organize code, improve code reusability, and make it easier to maintain and debug. PHP provides a range of built-in functions and also allows users to create their own custom functions.
11. What are the different types of variables in PHP?
There are several types of variables in PHP. The basic variable types include integers (whole numbers), floats (decimal numbers), strings (sequences of characters), booleans (true or false values), and arrays (ordered collections of values).
Additionally, PHP supports more complex data types such as objects (instances of classes), resources (references to external resources), and null (variables with no value assigned).
12. What is the difference between require() and include() in PHP?
Here are the major differences between require() and include() functions in PHP:
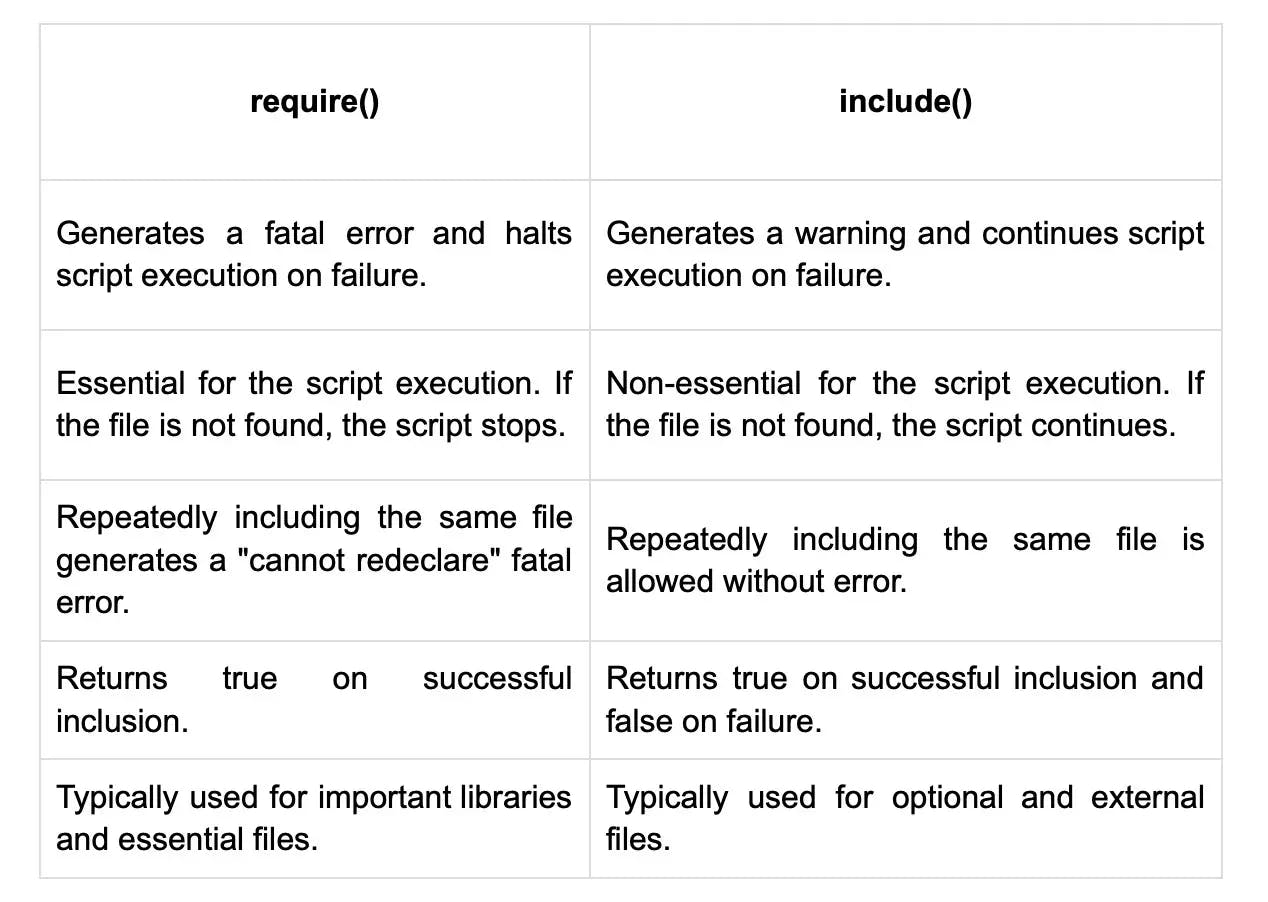
Note: Both require() and include() are used for including external PHP files into another PHP file. The main difference lies in their error handling and how they handle file inclusion failures.
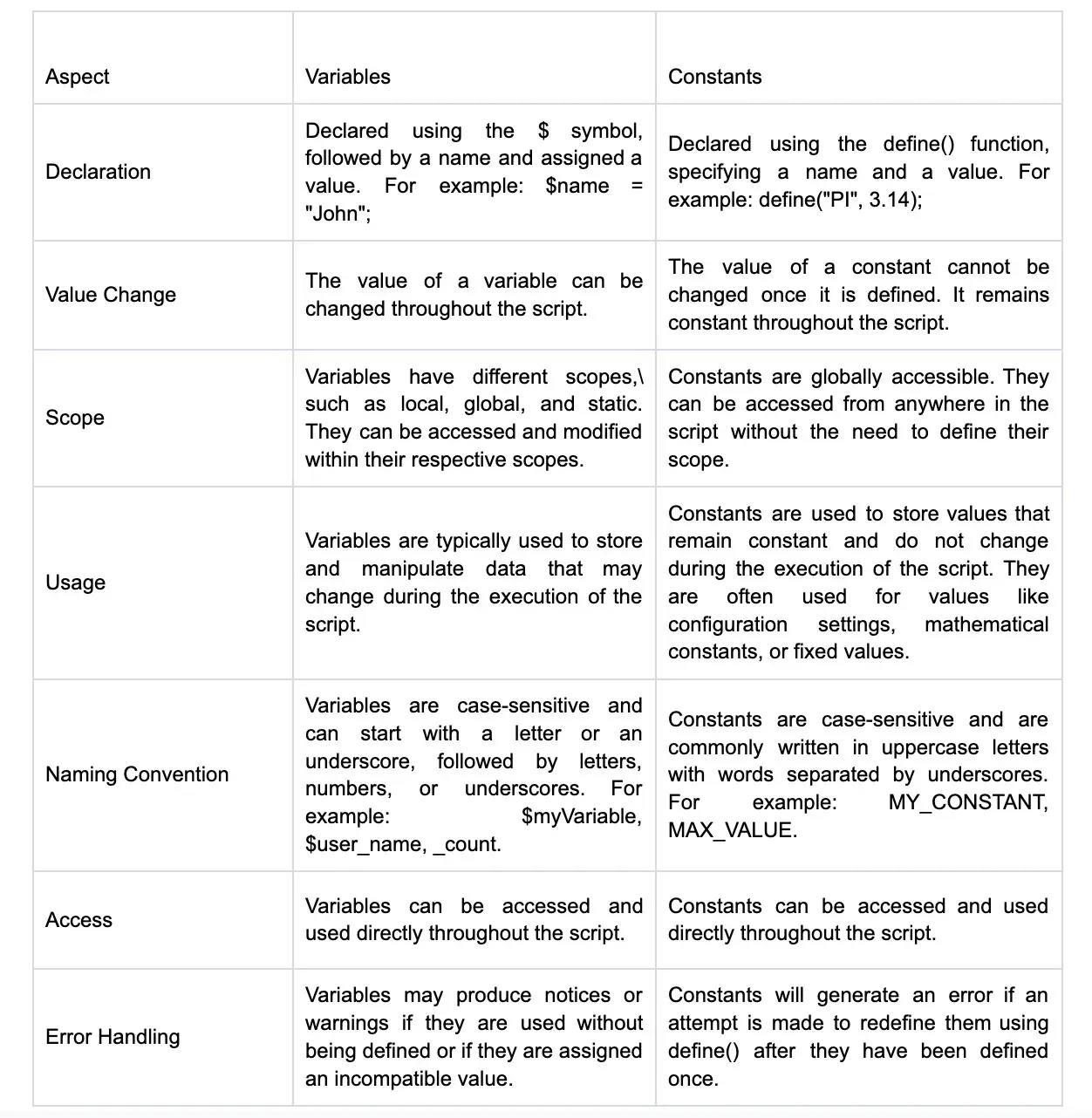
13. What is the syntax for defining a constant in PHP?
In PHP, constants are defined using the define() function or the const keyword. The define() function syntax is:
define('CONSTANT_NAME', value, case_insensitive);
The const keyword syntax is:
const CONSTANT_NAME = value;
Replace CONSTANT_NAME with the desired name of the constant. It should follow the naming conventions for PHP variables. Replace value with the actual value you want to assign to the constant. For the define() function, the optional case_insensitive parameter is a boolean value that determines whether the constant name should be treated as case-insensitive. If set to true, the constant name can be used in any case (upper, lower, or mixed). If omitted or set to false, the constant name is case-sensitive, and its usage must match the case defined during its declaration.
14. How do you declare a variable in PHP?
In PHP, you can declare a variable using the dollar sign ($) followed by the variable name. You don't need to specify the variable type explicitly. For example, to declare a variable called "name" and assign it a value, you would write: $name = "John";
15. What is the difference between echo and print in PHP?
In PHP, both echo and print are used to output data. echo is a language construct and does not require parentheses. It can output multiple strings at once, separated by commas. print is a function in PHP and must be used with parentheses. It can only output a single string at a time.
echo does not have a return value. It means that echo does not return anything and, therefore, cannot be used as part of an expression. On the other hand, print returns 1 after outputting the string successfully. This makes it different from echo, which does not have a return value.
16. What are the different types of Array in PHP?
There are three main types of arrays of PHP: indexed arrays, associative arrays, and multidimensional arrays.
- Indexed arrays use numeric keys to access elements and are created using square brackets ([]).
- Associative arrays use key-value pairs, where keys are strings, and elements are accessed using the keys.
- Multidimensional arrays are arrays that contain other arrays, creating a hierarchical structure with multiple levels of nesting.
17. What is a PHP session?
A PHP session is a mechanism that allows you to store and retrieve data for a user across multiple requests. It enables the server to maintain stateful information about the user. When a session is started, a unique session ID is generated and stored on the user's browser, while the associated data is stored on the server. This enables persistent data storage and user tracking during a browsing session.
18. What is a for loop in PHP?
In PHP, a for loop is a control structure used for iterative execution. It allows you to execute a block of code a specific number of times. The for loop consists of three parts: initialization, condition, and increment/decrement.
It follows the syntax
for (initialization; condition; increment/decrement) { // code }
where the initialization sets the starting value, the condition defines the loop termination, and the increment/decrement updates the loop variable in each iteration.
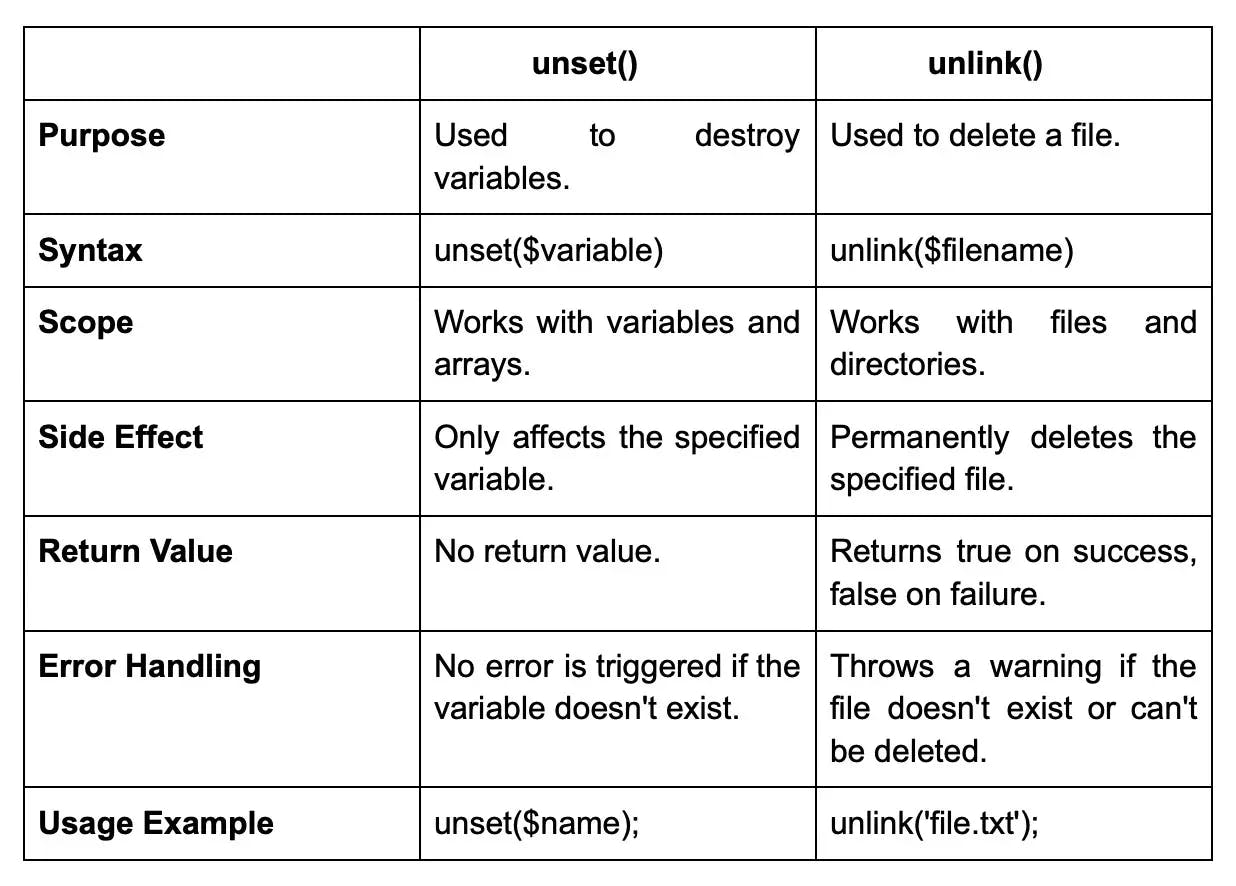
19. What is the difference between unset() and unlink() in PHP?
The difference between unset() and unlink() in PHP is:
20. How do you start a PHP session?
To start a PHP session, you can use the session_start() function. This function initializes a new or existing session and allows you to store and retrieve data across multiple pages.
Call session_start() at the beginning of your PHP script. You can then set session variables and access them throughout your application.
21. What is the purpose of the :: operator in PHP?
In PHP, the double colon (::) operator is called the scope resolution operator. It is used to access static methods, properties, and constants of a class without the need for an instance of that class. It allows for direct access to class-level elements, providing a way to organize and utilize shared resources across different instances of the same class.
22. How do you destroy a PHP session?
To destroy a PHP session, you can use the session_destroy() function. This function terminates the current session and removes all session data.
Additionally, you can unset individual session variables using the unset() function. After calling session_destroy(), the session is no longer available and a new session can be started if needed.
23. What is a PHP cookie?
A PHP cookie is a small piece of data stored on the user's computer by the web server. It is sent along with each request from the browser to the server, allowing the server to identify and personalize the user experience. Cookies are commonly used to store user preferences, session IDs, and other information. They can be set, accessed, and modified using PHP's setcookie() and $_COOKIE superglobal variables, respectively.
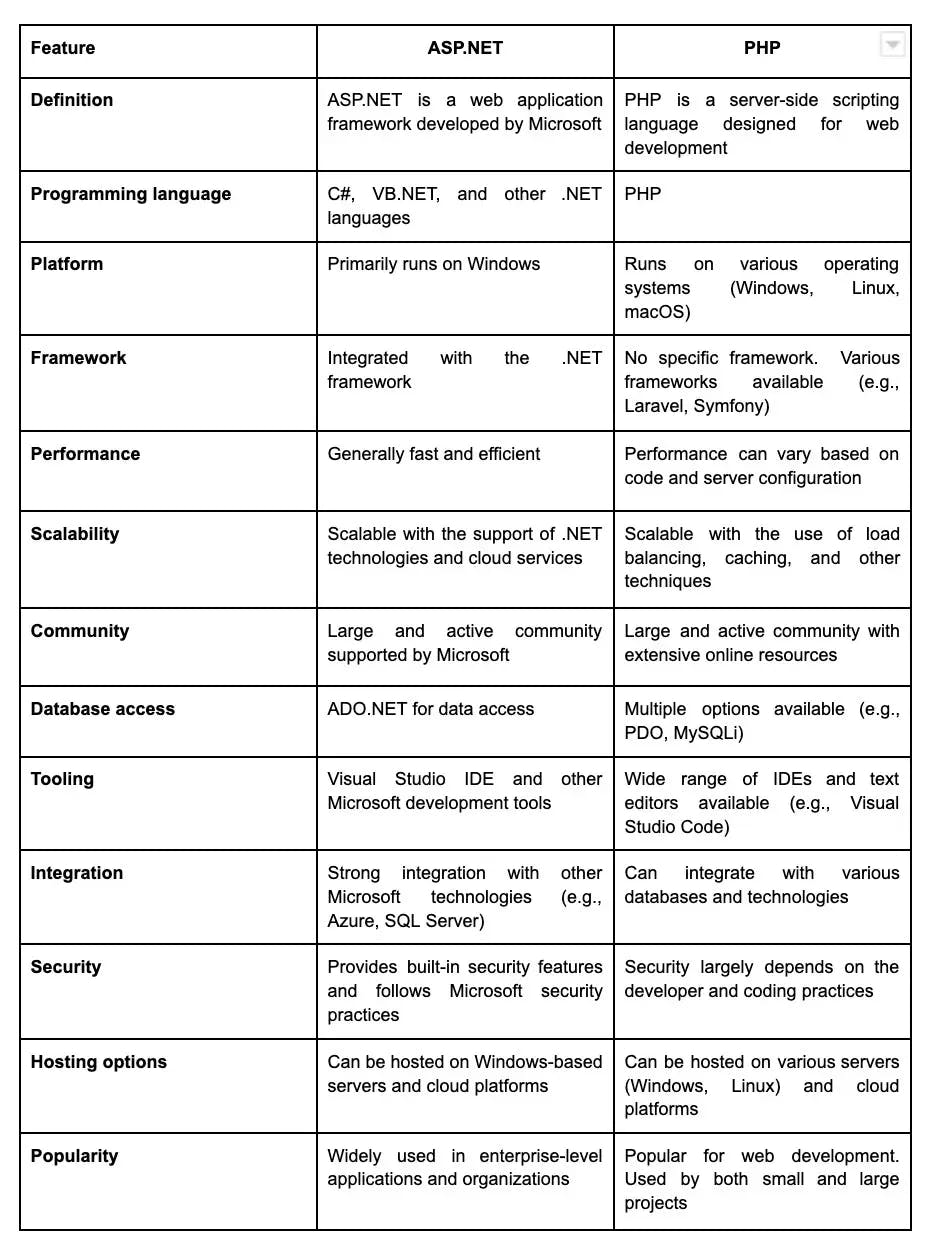
24. What is the difference between ASP.NET and PHP?
Here are the differences between ASP.NET and PHP:
25. What is the syntax for a foreach loop in PHP?
In PHP, the syntax for a foreach loop is as follows:

In this syntax:
$array is the array you want to iterate over.
$value is a variable that represents the current element of the array in each iteration. You can choose any valid variable name for this.
the code within the curly braces {} is the block of code that will be executed for each element in the array.
26. How do you create a PHP cookie?
To create a PHP cookie, you can use the setcookie() function. It takes multiple parameters including the cookie name, value, expiration time, path, domain, and whether the cookie should be sent over HTTPS only.
You can set the desired cookie values by providing these parameters. Once set, the cookie will be stored on the user's browser and sent with subsequent requests to the server.
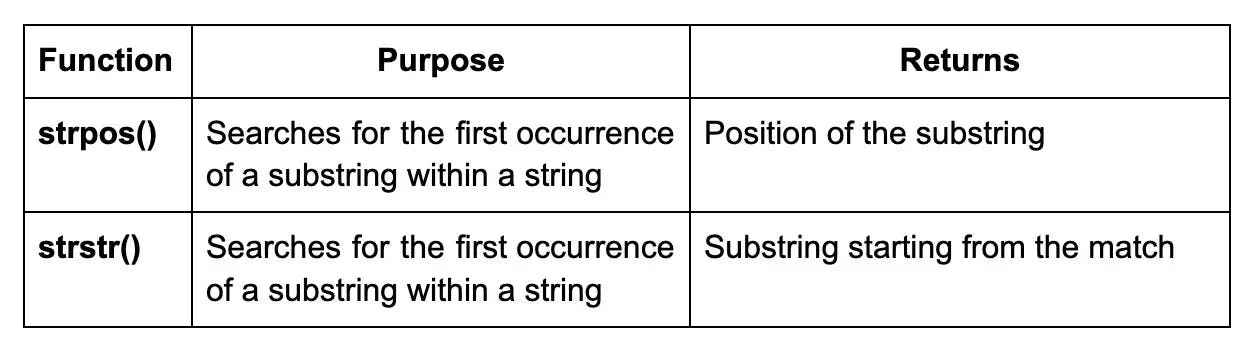
27. What is the difference between strpos() and strstr() in PHP?
The differences between strpos() and strstr() in PHP are:
28. Write the common applications of using include and require in PHP?
In PHP, include and require are used to import code from other PHP files into the current script. The common applications of using them are modularity and code reusability. Include allows the script to continue running even if the included file is missing or fails to load, making it suitable for optional components. Conversely, require is used for essential components, halting execution if the file is missing or fails to load.
These constructs are invaluable in breaking large codebases into smaller, manageable pieces, promoting maintainability and reducing redundancy by reusing code across multiple files or projects.
29. How to get the file extension in PHP?

30. What is a namespace in PHP?
In PHP, a namespace is a way to organize and encapsulate code elements, such as classes, functions, and constants, to avoid naming conflicts. It provides a hierarchical structure for declaring and accessing these elements.
Using namespaces, you can group related code together and ensure the uniqueness of names across different parts of your application or between libraries. Namespaces are declared using the namespace keyword.
31. What is an abstract class in PHP?
In PHP, an abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated directly and serves as a blueprint for derived classes. It is defined using the abstract keyword.
Abstract classes may contain abstract methods which are declared but not implemented in the abstract class itself. Derived classes must provide implementations for these abstract methods. Abstract classes are useful for creating a common interface and enforcing method implementation in derived classes.
32. What is an interface in PHP?
In PHP, an interface is a contract that defines a set of methods that a class must implement. It specifies the method names, parameters, and return types without providing the actual implementation. Classes can implement multiple interfaces, allowing them to fulfill multiple contracts simultaneously.
Interfaces enable the achievement of abstraction, polymorphism, and code reusability by ensuring consistency and providing a clear contract for interacting with objects.
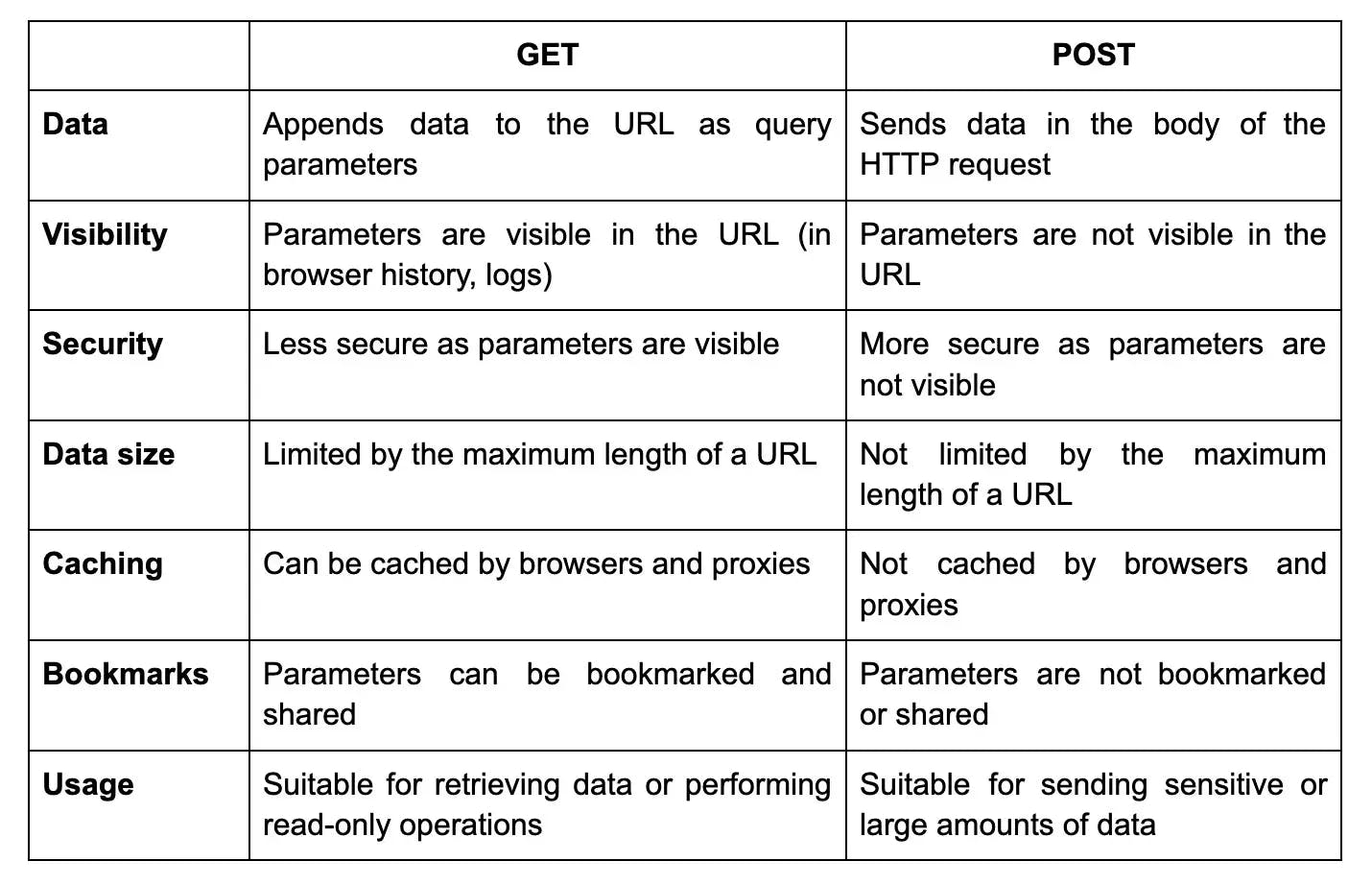
33. What is the difference between GET and POST methods in PHP?
The differences between GET and POST methods in PHP are:
34. What is the syntax for defining a function in PHP?
The syntax for defining a function in PHP is:
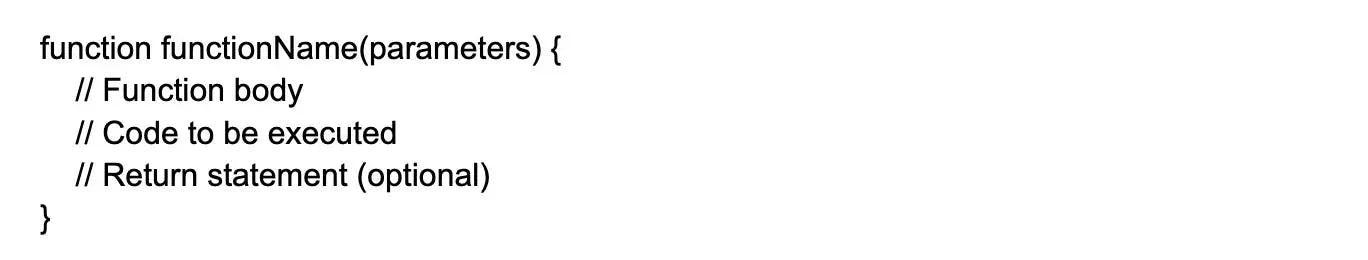
The function keyword is used to declare a function, followed by the function name and a pair of parentheses containing any parameters the function accepts.
You can write the code to be executed inside the function body. Optionally, you can use a return statement to return a value from the function.
35. What is a trait in PHP?
In PHP, a trait is a mechanism that allows for code reuse in classes by providing a way to define methods that can be included in multiple classes. Traits are declared using the trait keyword and can contain methods, properties, and other class elements.
They can be used alongside inheritance to incorporate reusable code into classes without the limitations of single inheritance. Traits enable horizontal code composition and promote code modularity.

36. What is a static method in PHP?
In PHP, a static method is one that belongs to a class rather than an instance of that class. It can be accessed directly using the class name without needing to create an object of that class.
Static methods are declared using the static keyword and can only access other static properties or invoke other static methods within the class. They are commonly used for utility functions or operations that don't require object-specific data.
37. What is the use of the self keyword in PHP?
In PHP, the self keyword is used to refer to the current class within the class itself. It allows access to static properties, constants, and methods defined within the same class. Unlike $this, which refers to the current instance of the class, the self is used in the context of the class definition itself.
The self keyword is commonly used for accessing static members and invoking static methods.
38. What is the use of the static keyword in PHP?
In PHP, the static keyword is used to define properties and methods that belong to a class itself rather than its instances. Static members can be accessed directly using the class name without the need for object instantiation.
They are shared among all instances of the class and allow for the storage and retrieval of data at the class level. Static methods are commonly used for utility functions or operations that don't require object-specific data.
39. What is an anonymous function in PHP?
In PHP, an anonymous function, also known as a lambda function, is a function without a specified name. It can be defined inline and assigned to a variable or passed as an argument to another function.
Anonymous functions are useful for creating callbacks, implementing simple logic without creating a separate named function, and enabling functional programming concepts. They provide flexibility and concise code in certain scenarios as listed below:
Callback functions: Anonymous functions are commonly used as callback functions, which are functions that can be passed as arguments to other functions. For example, when working with array functions like array_map(), array_filter(), or usort(), you can use anonymous functions to define the logic on-the-fly without the need to create a separate named function.

Closures: Anonymous functions in PHP can be used to create closures. A closure is an anonymous function that captures variables from its surrounding scope, allowing you to use those variables within the function, even if they are not passed as arguments explicitly.

Event handling: When dealing with event-driven programming or handling events in frameworks, anonymous functions are often used to define actions that should be executed when an event occurs.

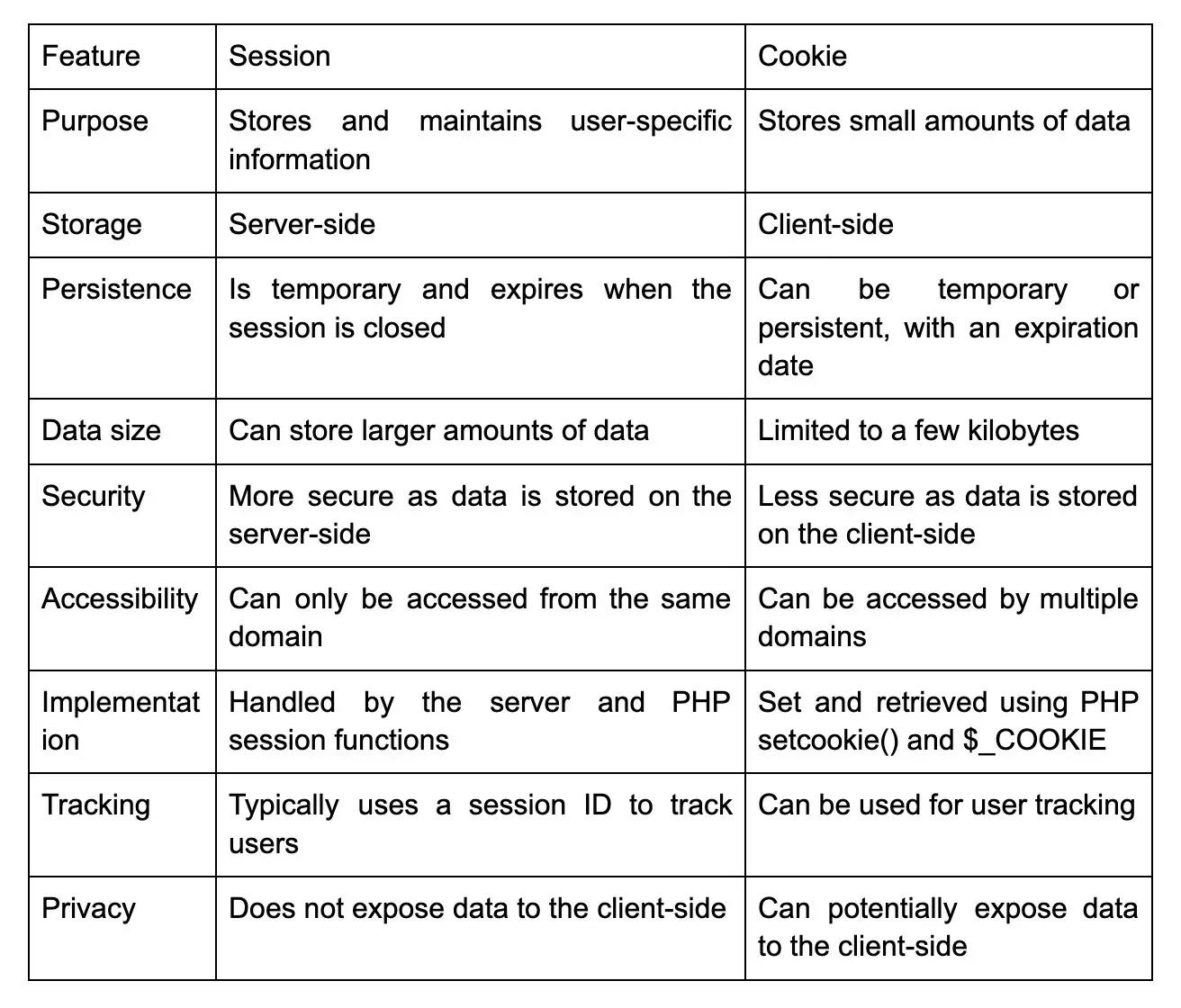
40. What is the difference between session and cookie in PHP?
Session and cookie have several differences:
41. What is the syntax for declaring a variable in PHP?
The syntax for declaring a variable in PHP is:

The dollar sign ($) is used to indicate that a variable is being declared. After the dollar sign, you provide a name for the variable, followed by an equal sign (=) and the value you want to assign to the variable. The value can be a literal value (e.g., a string, number) or the result of an expression.
42. What is a closure in PHP?
In PHP, a closure, also known as an anonymous function with access to its own scope, is a special type of function that can capture and retain the environment in which it was defined. It allows the function to access variables from its surrounding scope, even after the outer function has finished executing.
Closures are commonly used for creating callbacks, implementing higher-order functions, and providing encapsulation of functionality.
43. What is a generator in PHP?
In PHP, a generator is a special type of function that allows you to iterate over a set of values without needing to generate and store all the values in memory at once. It uses the yield keyword to produce a sequence of values on each iteration.
Generators are memory-efficient and useful for working with large or infinite sequences such as database results and streaming data.
44. What is the difference between an array and a list in PHP?
An array in PHP is a data structure that stores an ordered collection of elements. It can be accessed using numerical indices or associative keys. PHP arrays can contain elements of different data types, and they are dynamic, meaning you can add or remove elements as needed. Arrays in PHP are versatile and commonly used for various tasks, such as storing sets of data, implementing data structures, and managing collections.
In PHP, a list is not a distinct data structure. However, developers sometimes refer to an array with consecutive numeric indices (0, 1, 2, ...) as a list. Essentially, a list-like behavior can be achieved using a numeric array with consecutive integer keys starting from 0. PHP arrays can be treated as lists when the keys are used as indices to access elements.
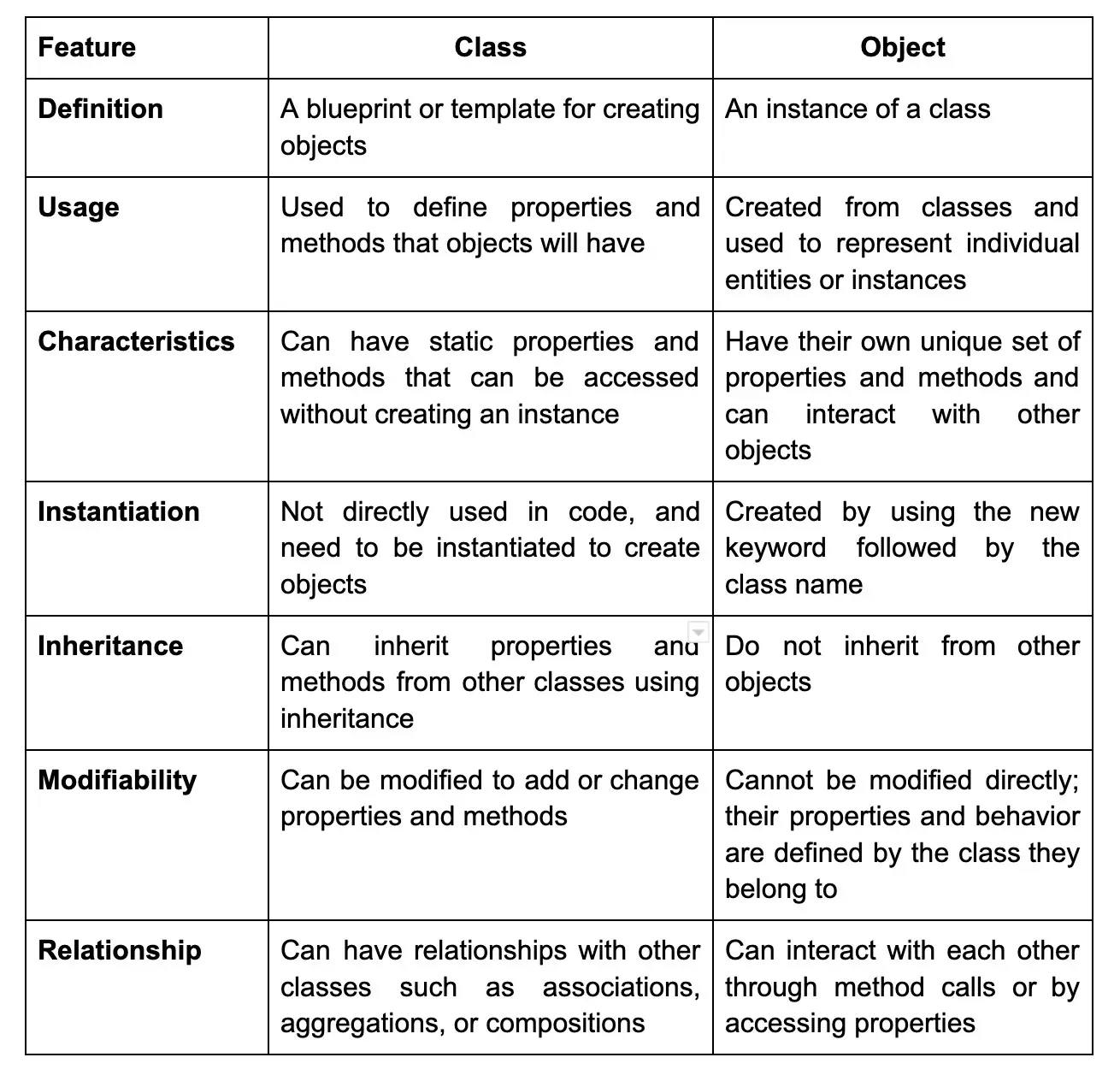
45. What is the difference between class and object in PHP?
The differences between class and object in PHP are as follows:
Wrapping up
This list of 100 PHP technical interview questions will help you prepare for upcoming interviews, especially for technical rounds. Brush up your knowledge by going through them. Do note, however, that they may not be the sole focus of a PHP interview.
Recruiters may also ask questions about a candidate’s skills, past responsibilities, and accomplishments to find out whether they are a fit for their job roles.
If you're a recruiter trying to hire from the top 1% of PHP developers, Turing.com is your go-to source. Turing.com is also an excellent place for experienced PHP developers looking for new career opportunities.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber PHP developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.